Effect of Intravesical Instillation of Gemcitabine vs Saline Immediately Following Resection of Suspected Low-Grade Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer on Tumor Recurrence: SWOG S0337 Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 29801011
- PMCID: PMC6583489
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2018.4657
Effect of Intravesical Instillation of Gemcitabine vs Saline Immediately Following Resection of Suspected Low-Grade Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer on Tumor Recurrence: SWOG S0337 Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Low-grade non-muscle-invasive urothelial cancer frequently recurs after excision by transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT).
Objective: To determine whether immediate post-TURBT intravesical instillation of gemcitabine reduces recurrence of suspected low-grade non-muscle-invasive urothelial cancer compared with saline.
Design, setting, and participants: Randomized double-blind clinical trial conducted at 23 US centers. Patients with suspected low-grade non-muscle-invasive urothelial cancer based on cystoscopic appearance without any high-grade or without more than 2 low-grade urothelial cancer episodes within 18 months before index TURBT were enrolled between January 23, 2008, and August 14, 2012, and followed up every 3 months with cystoscopy and cytology for 2 years and then semiannually for 2 years. Patients were monitored for tumor recurrence, progression to muscle invasion, survival, and toxic effects. The final date of follow-up was August 14, 2016.
Interventions: Participants were randomly assigned to receive intravesical instillation of gemcitabine (2 g in 100 mL of saline) (n = 201) or saline (100 mL) (n = 205) for 1 hour immediately following TURBT.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome was time to recurrence of cancer. Secondary end points were time to muscle invasion and death due to any cause.
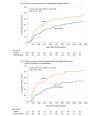
Results: Among 406 randomized eligible patients (median age, 66 years; 84.7% men), 383 completed the trial. In the intention-to-treat analysis, 67 of 201 patients (4-year estimate, 35%) in the gemcitabine group and 91 of 205 patients (4-year estimate, 47%) in the saline group had cancer recurrence within 4.0 years (hazard ratio, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.48-0.90; P<.001 by 1-sided log-rank test for time to recurrence). Among the 215 patients with low-grade non-muscle-invasive urothelial cancer who underwent TURBT and drug instillation, 34 of 102 patients (4-year estimate, 34%) in the gemcitabine group and 59 of 113 patients (4-year estimate, 54%) in the saline group had cancer recurrence (hazard ratio, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.35-0.81; P = .001 by 1-sided log-rank test for time to recurrence). Fifteen patients had tumors that progressed to muscle invasion (5 in the gemcitabine group and 10 in the saline group; P = .22 by 1-sided log-rank test) and 42 died of any cause (17 in the gemcitabine group and 25 in the saline group; P = .12 by 1-sided log-rank test). There were no grade 4 or 5 adverse events and no significant differences in adverse events of grade 3 or lower.
Conclusions and relevance: Among patients with suspected low-grade non-muscle-invasive urothelial cancer, immediate postresection intravesical instillation of gemcitabine, compared with instillation of saline, significantly reduced the risk of recurrence over a median of 4.0 years. These findings support using this therapy, but further research is needed to compare gemcitabine with other intravesical agents.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT00445601.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Simplifying Treatment and Reducing Recurrence for Patients With Early-Stage Bladder Cancer.JAMA. 2018 May 8;319(18):1864-1865. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.4656. JAMA. 2018. PMID: 29800998 No abstract available.
-
Gemcitabine reduces recurrence.Nat Rev Urol. 2018 Aug;15(8):466. doi: 10.1038/s41585-018-0033-x. Nat Rev Urol. 2018. PMID: 29849109 No abstract available.
-
Re: Effect of Intravesical Instillation of Gemcitabine vs Saline Immediately Following Resection of Suspected Low-grade Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer on Tumor Recurrence.Eur Urol. 2019 Feb;75(2):341-342. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.10.035. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Eur Urol. 2019. PMID: 30391080 No abstract available.
-
Re: Effect of Intravesical Instillation of Gemcitabine vs Saline Immediately following Resection of Suspected Low-Grade Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer on Tumor Recurrence:J Urol. 2019 Mar;201(3):442. doi: 10.1097/01.JU.0000553700.73423.cb. J Urol. 2019. PMID: 30759672 No abstract available.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(1):7-30. - PubMed
-
- Messing EM, Madeb R, Young T, et al. . Long-term outcome of hematuria home screening for bladder cancer in men. Cancer. 2006;107(9):2173-2179. - PubMed
-
- Botteman MF, Pashos CL, Redaelli A, Laskin B, Hauser R. The health economics of bladder cancer: a comprehensive review of the published literature. Pharmacoeconomics. 2003;21(18):1315-1330. - PubMed
-
- Babjuk M, Böhle A, Burger M, et al. . EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2016. Eur Urol. 2017;71(3):447-461. - PubMed
-
- Chang SS, Boorjian SA, Chou R, et al. . Diagnosis and treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: AUA/SUO guideline. J Urol. 2016;196(4):1021-1029. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 CA180834/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233329/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180801/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180818/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233340/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 CA233374/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA022433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA093373/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA128567/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180846/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA068183/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189854/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180819/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189953/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

