Anti-apoptotic Protein BIRC5 Maintains Survival of HIV-1-Infected CD4+ T Cells
- PMID: 29802019
- PMCID: PMC6013384
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.04.004
Anti-apoptotic Protein BIRC5 Maintains Survival of HIV-1-Infected CD4+ T Cells
Abstract
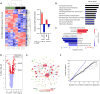
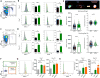
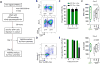
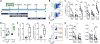
HIV-1 infection of CD4+ T cells leads to cytopathic effects and cell demise, which is counter to the observation that certain HIV-1-infected cells possess a remarkable long-term stability and can persist lifelong in infected individuals treated with suppressive antiretroviral therapy (ART). Using quantitative mass spectrometry-based proteomics, we showed that HIV-1 infection activated cellular survival programs that were governed by BIRC5, a molecular inhibitor of cell apoptosis that is frequently overexpressed in malignant cells. BIRC5 and its upstream regulator OX40 were upregulated in productively and latently infected CD4+ T cells and were functionally involved in maintaining their viability. Moreover, OX40-expressing CD4+ T cells from ART-treated patients were enriched for clonally expanded HIV-1 sequences, and pharmacological inhibition of BIRC5 resulted in a selective decrease of HIV-1-infected cells in vitro. Together, these findings suggest that BIRC5 supports long-term survival of HIV-1-infected cells and may lead to clinical strategies to reduce persisting viral reservoirs.
Keywords: BIRC5; HIV-1; OX40; Survivin; apoptosis; clonal proliferation; latency; proteomics; viral reservoirs.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that conflicts of interests do not exist.
Figures

Comment in
-
Cheating cell death.Nat Rev Immunol. 2018 Jul;18(7):418-419. doi: 10.1038/s41577-018-0026-2. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29802385 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC. A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nature medicine. 1997;3:917–921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AI106468/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI078799/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134539/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI114235/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI098487/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI130005/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI117841/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI125109/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R33 AI116228/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI124776/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI120008/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI116228/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD012027/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI060354/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

