Characterization of the Open-Label Lead-In Period of Two Randomized Controlled Phase 3 Trials Evaluating Dapagliflozin, Saxagliptin, and Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 29802530
- PMCID: PMC6064585
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-018-0445-x
Characterization of the Open-Label Lead-In Period of Two Randomized Controlled Phase 3 Trials Evaluating Dapagliflozin, Saxagliptin, and Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Introduction: To examine the utility of sequential versus dual add-on approaches in patients who have type 2 diabetes and inadequate glycemic control with metformin therapy alone, we characterized the efficacy and safety of dual therapy with dapagliflozin or saxagliptin added to metformin in the open-label lead-in periods of two phase 3 trials (study 1, NCT01619059; study 2, NCT01646320) that evaluated triple therapy in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes.
Methods: During the lead-in periods of each trial, patients [glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) 8.0-11.5%] who had been receiving metformin ≥ 1500 mg/day for ≥ 8 weeks received metformin immediate release at an equivalent dose plus dapagliflozin 10 mg/day (study 1; N = 482) or saxagliptin 5 mg/day (study 2; N = 349) for 16 weeks. Efficacy end points were assessed at week - 2 before randomization.
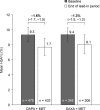
Results: Mean change in HbA1c [95% confidence interval (CI)] from lead-in baseline (study 1, 9.3%; study 2, 9.4%) was - 1.6% (- 1.7, - 1.5) in study 1 and - 1.3% (- 1.5, - 1.2) in study 2. Mean changes (95% CI) from lead-in baseline in weight and fasting plasma glucose were - 2.4 kg (- 2.6, - 2.1) and - 47.5 mg/dL (- 52.8, - 42.3) for study 1 and - 0.5 kg (- 0.8, - 0.2) and - 28.5 mg/dL (- 35.8, - 21.2) for study 2. At the end of the lead-in period, 22.0% of patients achieved HbA1c < 7.0% in study 1 and 17.5% in study 2. Dual therapy was well tolerated, with hypoglycemia incidence < 1% in both studies.
Conclusion: Dual therapy improved glycemic control and was well tolerated; however, most patients required additional therapy to further improve HbA1c towards target, suggesting that an early move to triple therapy with oral glucose-lowering drugs rather than a stepwise approach may be beneficial for patients with high HbA1c levels on metformin therapy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01619059, NCT01646320.
Funding: AstraZeneca.
Keywords: Dapagliflozin; Dual therapy; Saxagliptin; Triple therapy; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures

References
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centred approach. Update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetologia. 2015;58:429–442. doi: 10.1007/s00125-014-3460-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, et al. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm—2016 executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2016;22:84–113. doi: 10.4158/EP151126.CS. - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association Standards of medical care in diabetes—2017. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(Suppl 1):S1–S132. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

