The long non-coding RNA PTTG3P promotes cell growth and metastasis via up-regulating PTTG1 and activating PI3K/AKT signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 29803224
- PMCID: PMC5970477
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-018-0841-x
The long non-coding RNA PTTG3P promotes cell growth and metastasis via up-regulating PTTG1 and activating PI3K/AKT signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
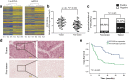
Background: Dysfunctions of long non-coding RNA (lncRNAs) have been associated with the initiation and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but the clinicopathologic significance and potential role of lncRNA PTTG3P (pituitary tumor-transforming 3, pseudogene) in HCC remains largely unknown.
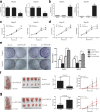
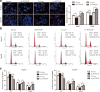
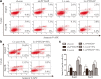
Methods: We compared the expression profiles of lncRNAs in 3 HCC tumor tissues and adjacent non-tumor tissues by microarrays. In situ hybridization (ISH) and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) were applied to assess the level of PTTG3P and prognostic values of PTTG3P were assayed in two HCC cohorts (n = 46 and 90). Artificial modulation of PTTG3P (down- and over-expression) was performed to explore the role of PTTG3P in tumor growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Involvement of PTTG1 (pituitary tumor-transforming 1), PI3K/AKT signaling and its downstream signals were validated by qRT-PCR and western blot.
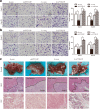
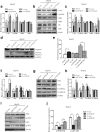
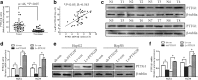
Results: We found that PTTG3P was frequently up-regulated in HCC and its level was positively correlated to tumor size, TNM stage and poor survival of patients with HCC. Enforced expression of PTTG3P significantly promoted cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro, as well as tumorigenesis and metastasis in vivo. Conversely, PTTG3P knockdown had opposite effects. Mechanistically, over-expression of PTTG3P up-regulated PTTG1, activated PI3K/AKT signaling and its downstream signals including cell cycle progression, cell apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-associated genes.
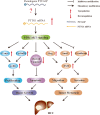
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that PTTG3P, a valuable marker of HCC prognosis, promotes tumor growth and metastasis via up-regulating PTTG1 and activating PI3K/AKT signaling in HCC and might represent a potential target for gene-based therapy.
Keywords: Hepatocellular Carcinoma; Long non-coding RNA; PI3K/AKT signaling; PTTG1; PTTG3P.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Written informed consent for the biological studies was obtained from each patient involved in the study, and the study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Nanfang Hospital. All animal studies were approved by the Animal Experimental Committee of Nanfang Hospital.
Consent for publication
Written consent for publication was obtained from all the patients involved in our study.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

