Landscape of Conditional eQTL in Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex and Co-localization with Schizophrenia GWAS
- PMID: 29805045
- PMCID: PMC5993513
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.04.011
Landscape of Conditional eQTL in Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex and Co-localization with Schizophrenia GWAS
Abstract
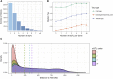
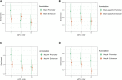
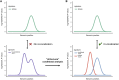
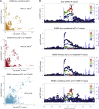
Causal genes and variants within genome-wide association study (GWAS) loci can be identified by integrating GWAS statistics with expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) and determining which variants underlie both GWAS and eQTL signals. Most analyses, however, consider only the marginal eQTL signal, rather than dissect this signal into multiple conditionally independent signals for each gene. Here we show that analyzing conditional eQTL signatures, which could be important under specific cellular or temporal contexts, leads to improved fine mapping of GWAS associations. Using genotypes and gene expression levels from post-mortem human brain samples (n = 467) reported by the CommonMind Consortium (CMC), we find that conditional eQTL are widespread; 63% of genes with primary eQTL also have conditional eQTL. In addition, genomic features associated with conditional eQTL are consistent with context-specific (e.g., tissue-, cell type-, or developmental time point-specific) regulation of gene expression. Integrating the 2014 Psychiatric Genomics Consortium schizophrenia (SCZ) GWAS and CMC primary and conditional eQTL data reveals 40 loci with strong evidence for co-localization (posterior probability > 0.8), including six loci with co-localization of conditional eQTL. Our co-localization analyses support previously reported genes, identify novel genes associated with schizophrenia risk, and provide specific hypotheses for their functional follow-up.
Keywords: GWAS co-localization; complex trait; conditional eQTL; eQTLs; expression quantitative trait loci; fine mapping; gene expression regulation; neuropsychiatric disorder; risk gene; schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Montgomery S.B., Dermitzakis E.T. From expression QTLs to personalized transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011;12:277–282. - PubMed
-
- Albert F.W., Kruglyak L. The role of regulatory variation in complex traits and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015;16:197–212. - PubMed
-
- Moffatt M.F., Kabesch M., Liang L., Dixon A.L., Strachan D., Heath S., Depner M., von Berg A., Bufe A., Rietschel E. Genetic variants regulating ORMDL3 expression contribute to the risk of childhood asthma. Nature. 2007;448:470–473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 AG046152/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH090047/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH109536/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH084053/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201300031C/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH080405/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH057881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH075916/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089921/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX002395/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 MH097276/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG002219/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH093725/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH066392/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089929/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG036836/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085542/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

