Protective mechanism of sulforaphane in Nrf2 and anti-lung injury in ARDS rabbits
- PMID: 29805514
- PMCID: PMC5952085
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6036
Protective mechanism of sulforaphane in Nrf2 and anti-lung injury in ARDS rabbits
Abstract
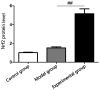
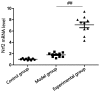
The effect of sulforaphane on nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and its protective mechanism for lung injury in rabbits with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) were investigated. Thirty rabbits were randomly divided into control (n=10), model (n=10) and experimental groups (n=10). Rabbits in model group and experimental group were treated with femoral venous injection of oleic acid to establish the ARDS model, while those in control group were injected with the same volume of normal saline. The experimental group received intravenous injection of sulforaphane. Twelve hours after modeling, the clinical manifestations and deaths of rabbits in each group were recorded and compared, including blood gas indexes, lung index (LI), alveolar damage coefficient, serum Nrf2 expression, as well as messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) and protein expression of Nrf2 in lung tissues. Pink frothy sputum and death were observed in rabbits in model group and experimental group, but the number of such cases in experimental group was smaller than that in the model group (p<0.05). Compared with those in control group, LI and IQA in model group and experimental group were increased, but LI and IQA in the experimental group were significantly decreased compared with those in the model group. Compared with those in the model group, the blood gas indexes (PaO2, PaCO2 and SaO2) in the experimental group were significantly increased (p<0.05). Nrf2 in serum and lung tissues of rabbits in experimental group was significantly increased compared with that in model group (p<0.05). Sulforaphane significantly inhibits ARDS in rabbits and plays a protective role in ARDS through upregulating Nrf2.
Keywords: Nrf2; acute lung injury; acute respiratory distress syndrome; mRNA; sulforaphane.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Effects of mechanical ventilation with different tidal volumes on coagulation/fibrinolysis in rabbits with acute respiratory distress syndrome].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015 Jul;27(7):585-90. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2015.07.009. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015. PMID: 26138421 Chinese.
-
Xuebijing injection improves the respiratory function in rabbits with oleic acid-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting IL-6 expression and promoting IL-10 expression at the protein and mRNA levels.Exp Ther Med. 2014 Nov;8(5):1593-1598. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.1949. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Exp Ther Med. 2014. PMID: 25289065 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparison of lung protection for hydrochloric acid or oleic acid induced rat acute respiratory distress syndrome models pretreated with penehyclidine].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 May;30(5):434-438. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.05.008. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 29764547 Chinese.
-
[The changes in effective local blood perfusion and compensatory ventilation in different lung areas of acute respiratory distress syndrome rabbits model].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2004 Jul;43(7):522-6. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15312408 Chinese.
-
[Research progress of nuclear factor-erythroid 2 related factor 2 in acute lung injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Mar;30(3):270-274. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.03.016. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 29519289 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Nrf-2 as a novel target in radiation induced lung injury.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 10;10(8):e29492. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29492. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38665580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Role of Nrf2 Activators with Dual Antiviral and Anti-Inflammatory Properties in the Management of Viral Pneumonia.Infect Drug Resist. 2020 Jun 11;13:1735-1741. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S256773. eCollection 2020. Infect Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 32606823 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Antioxidants Significantly Attenuate Hyperoxia-Induced Acute Inflammatory Lung Injury by Enhancing Macrophage Function via Reducing the Accumulation of Airway HMGB1.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 1;21(3):977. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030977. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32024151 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor NF-E2-related factor 2 plays a critical role in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome (ALI/ARDS) by regulating ferroptosis.PeerJ. 2024 Jul 30;12:e17692. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17692. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39670103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Argan Oil: A Natural Bioactive Lipid Modulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Apr 25;14(5):515. doi: 10.3390/antiox14050515. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427397 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thille AW, Esteban A, Fernández-Segoviano P, Rodriguez JM, Aramburu JA, Vargas-Errázuriz P, Martín-Pellicer A, Lorente JA, Frutos-Vivar F. Chronology of histological lesions in acute respiratory distress syndrome with diffuse alveolar damage: A prospective cohort study of clinical autopsies. Lancet Respir Med. 2013;1:395–401. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(13)70053-5. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
