Application value of CT and MRI in diagnosis of primary brain lymphoma
- PMID: 29805587
- PMCID: PMC5950549
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.8404
Application value of CT and MRI in diagnosis of primary brain lymphoma
Abstract
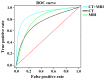
This study explored the correlation between computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) manifestations and pathological features of primary brain lymphoma to improve the diagnostic accuracy. A total of 230 patients with primary brain lymphoma admitted to People's Hospital of Rizhao from July, 2005 to December, 2016 were selected into the study and their clinical data were analyzed retrospectively. Among them, 87 patients were examined by CT, 74 patients by MRI, 69 patients by both MRI and CT. Features of MRI and CT scanning figures were observed with a focus on the density, number and margins of the lesions, and the diagnostic accuracy was analyzed. A total of 353 lesions were identified from 230 primary brain lymphoma patients, of which 224 were single lesions, and 129 were multiple lesions. Most lesions were on the upper curtain (81.3%, 187 cases) and 43 cases (18.7%) were on the lower curtain. Lesion signal of CT and MRI plain scan showed uniform state, and enhanced scan showed significantly enhanced signal. Diagnostic accuracy of CT was 82.8%, and sensitivity and specificity was 75.5 and 67.4%, respectively. Diagnostic accuracy of MRI was 83.8%, and sensitivity and specificity was 79.3 and 64.9%, respectively. Diagnostic accuracy of MRI combined with CT was 89.9%, and sensitivity and specificity was 86.3 and 75.8%, respectively. CT combined with MRI can provide better diagnosis for primary brain lymphoma compared with CT or MRI alone, but pathological test is still needed.
Keywords: application; computed tomography; diagnosis; magnetic resonance imaging; primary brain lymphoma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[CT and MRI manifestation of primary spinal large B cell lymphoma].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2017 Dec 25;30(12):1141-1146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0034.2017.12.013. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2017. PMID: 29457438 Chinese.
-
More advantages in detecting bone and soft tissue metastases from prostate cancer using 18F-PSMA PET/CT.Hell J Nucl Med. 2019 Jan-Apr;22(1):6-9. doi: 10.1967/s002449910952. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Hell J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 30843003
-
The added value of PET/Ce-CT/DW-MRI fusion in assessment of hepatic focal lesions: PET/Ce-CT/DW-MRI fusion in hepatic focal lesion.Nucl Med Biol. 2015 Jul;42(7):637-42. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2015.03.010. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Nucl Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 25907467
-
Diagnostic performance of CT, gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI, and PET/CT for the diagnosis of colorectal liver metastasis: Systematic review and meta-analysis.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018 May;47(5):1237-1250. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25852. Epub 2017 Sep 13. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018. PMID: 28901685
-
[CT and MRI in the differential diagnosis of lesions of the adrenal gland].Med Klin (Munich). 2004 Aug 15;99(8):447-52. doi: 10.1007/s00063-004-1054-1. Med Klin (Munich). 2004. PMID: 15309273 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the Effects of Folic Acid Combined with Atorvastatin on the Poststroke Cognitive Impairment by Low-Rank Matrix Denoising Algorithm-Based MRI Imaging.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Mar 4;2022:9540701. doi: 10.1155/2022/9540701. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35317130 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of radiology modalities in diagnosing and characterizing brain disorders.Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2024 Jan;29(1):37-43. doi: 10.17712/nsj.2024.1.20230048. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2024. PMID: 38195124 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted multiplex validation of CSF proteomic biomarkers: implications for differentiation of PCNSL from tumor-free controls and other brain tumors.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 1;15:1343109. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1343109. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39144147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoang-Xuan K, Bessell E, Bromberg J, Hottinger AF, Preusser M, Rudà R, Schlegel U, Siegal T, Soussain C, Abacioglu U, et al. European Association for Neuro-Oncology Task Force on Primary CNS Lymphoma: Diagnosis and treatment of primary CNS lymphoma in immunocompetent patients: Guidelines from the European Association for Neuro-Oncology. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:e322–e332. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00076-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ferreri AJ, Cwynarski K, Pulczynski E, Ponzoni M, Deckert M, Politi LS, Torri V, Fox CP, Rosée PL, Schorb E, et al. International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group (IELSG): Chemoimmunotherapy with methotrexate, cytarabine, thiotepa, and rituximab (MATRix regimen) in patients with primary CNS lymphoma: Results of the first randomisation of the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group-32 (IELSG32) phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2016;3:e217–e227. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(16)00036-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nayak L, Pentsova E, Batchelor TT. Primary CNS lymphoma and neurologic complications of hematologic malignancies. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 2015;21:355–372. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
