miR-19 in blood plasma reflects lung cancer occurrence but is not specifically associated with radon exposure
- PMID: 29805621
- PMCID: PMC5950512
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.8392
miR-19 in blood plasma reflects lung cancer occurrence but is not specifically associated with radon exposure
Abstract
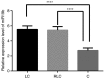
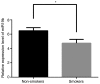
Radon is one of the most powerful carcinogens, particularly in terms of lung cancer onset and development. miRNAs may be considered not only as markers of the ongoing tumorigenesis but also as a hallmark of exposure to radiation, including radon and its progeny. Therefore, the purpose of the present study was to estimate the value of plasma miR-19b-3p level as the prospective marker of the response to radon exposure in lung cancer pathogenesis. A total of 136 subjects were examined, including 49 radon-exposed patients with lung cancer, 37 patients with lung cancer without radon exposure and 50 age/sex matched healthy controls. Total RNA from blood samples was extracted and used to detect miR-19b-3p expression via reverse transcription quantitative-polymerase chain reaction. The 2-ΔΔCq method was used to quantify the amount of relative miRNA. The plasma level of p53 protein was determined using a Human p53 ELISA kit. Plasma miR-19b-3p level was significantly higher in the patients with lung cancer groups, compared with the healthy control group (P<0.0001). No other statistically significant differences were determined in the expression level of plasma miR-19b-3p between patients diagnosed with lung cancer exposed to radon and not exposed to radon. The expression level of free circulating miR-19b-3p was higher in the group of non-smoking patients with lung cancer, compared with smokers with lung cancer. The miR-19b-3p was 1.4-fold higher in non-smokers than in smokers (P<0.05). No association between plasma levels of p53 protein and miR-19b-3p freely circulating in patients with lung cancer was observed. No other statistically significant differences were determined in the plasma p53 protein level between patients diagnosed with lung cancer exposed and not exposed to radon. These results indicated that detection of miR-19b-3p levels in plasma potentially could be exploited as a noninvasive method for the lung cancer diagnostics. However, this miRNA is not suitable as the precise marker for radon impact.
Keywords: biomarker; lung cancer; miRNA; p53; radon.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circulating MiR-16-5p and MiR-19b-3p as Two Novel Potential Biomarkers to Indicate Progression of Gastric Cancer.Theranostics. 2015 Apr 5;5(7):733-45. doi: 10.7150/thno.10305. eCollection 2015. Theranostics. 2015. PMID: 25897338 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic changes in circulating miRNA levels in response to antitumor therapy of lung cancer.Exp Lung Res. 2016;42(2):95-102. doi: 10.3109/01902148.2016.1155245. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Exp Lung Res. 2016. PMID: 26986825
-
Circulating miR-19b-3p as a Novel Prognostic Biomarker for Acute Heart Failure.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Oct 19;10(20):e022304. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.022304. Epub 2021 Oct 6. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34612058 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating MiR-19b-3p, MiR-134-5p and MiR-186-5p are Promising Novel Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(3):1015-29. doi: 10.1159/000443053. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26939053
-
Identification of differentially expressed circulating serum microRNA for the diagnosis and prognosis of Indian non-small cell lung cancer patients.Curr Probl Cancer. 2020 Aug;44(4):100540. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2020.100540. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Curr Probl Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32007320 Review.
Cited by
-
Contributions of Circulating microRNAs for Early Detection of Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 30;14(17):4221. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174221. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36077759 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-19b-3p promotes tumor progression of non-small cell lung cancer via downregulating HOXA9 and predicts poor prognosis in patients.Histol Histopathol. 2022 Aug;37(8):779-789. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-448. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Histol Histopathol. 2022. PMID: 35274735
-
Upregulation of microRNA-181a-5p increases the sensitivity of HS578T breast cancer cells to cisplatin by inducing vitamin D receptor-mediated cell autophagy.Oncol Lett. 2021 Apr;21(4):247. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12508. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33664811 Free PMC article.
-
MALAT1 affects hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial cell injury and autophagy by regulating miR-19b-3p/HIF-1α axis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2020 Mar;466(1-2):25-34. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03684-z. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31933110
-
Role of microRNAs in Lung Carcinogenesis Induced by Asbestos.J Pers Med. 2021 Feb 3;11(2):97. doi: 10.3390/jpm11020097. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33546236 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amin J, Sharif M, Yasmin M. Segmentation and classification of lung cancer: A review. Immunol Endo Metab Age Med Chem. 2016;16:82–99. doi: 10.2174/187152221602161221215304. - DOI
-
- Zeeb H, Shannon F. WHO handbook on indoor radon: A public health perspective. In: Zeeb H, Shannon F, editors. World Health Organization. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2009. pp. 3–21.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
