Development of a cell-based assay to identify hepatitis B virus entry inhibitors targeting the sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide
- PMID: 29805766
- PMCID: PMC5955094
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.25348
Development of a cell-based assay to identify hepatitis B virus entry inhibitors targeting the sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide
Abstract
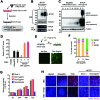
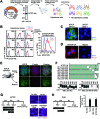
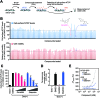
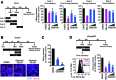
Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) is a major entry receptor of hepatitis B virus (HBV) and one of the most attractive targets for anti-HBV drugs. We developed a cell-mediated drug screening method to monitor NTCP expression on the cell surface by generating a HepG2 cell line with tetracycline-inducible expression of NTCP and a monoclonal antibody that specifically detects cell-surface NTCP. Using this system, we screened a small molecule library for compounds that protected against HBV infection by targeting NTCP. We found that glabridin, a licorice-derived isoflavane, could suppress viral infection by inducing caveolar endocytosis of cell-surface NTCP with an IC50 of ~40 μM. We also found that glabridin could attenuate the inhibitory effect of taurocholate on type I interferon signaling by depleting the level of cell-surface NTCP. These results demonstrate that our screening system could be a powerful tool for discovering drugs targeting HBV entry.
Keywords: HBV-permissive cell; ISG; anti-NTCP monoclonal antibody; glabridin; innate immune signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ott JJ, Stevens GA, Groeger J, Wiersma ST. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection: new estimates of age-specific HBsAg seroprevalence and endemicity. Vaccine. 2012;30:2212–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.12.116. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pawlotsky JM, Dusheiko G, Hatzakis A, Lau D, Lau G, Liang TJ, Locarnini S, Martin P, Richman DD, Zoulim F. Virologic monitoring of hepatitis B virus therapy in clinical trials and practice: recommendations for a standardized approach. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:405–15. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2007.11.036. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Janssen HL, van Zonneveld M, Senturk H, Zeuzem S, Akarca US, Cakaloglu Y, Simon C, So TM, Gerken G, de Man RA, Niesters HG, Zondervan P, Hansen B, et al. Pegylated interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2005;365:123–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)17701-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Papatheodoridis GV, Dimou E, Papadimitropoulos V. Nucleoside analogues for chronic hepatitis B: antiviral efficacy and viral resistance. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:1618–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05819.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li W, Urban S. Entry of hepatitis B and hepatitis D virus into hepatocytes: Basic insights and clinical implications. J Hepatol. 2016;64:S32–S40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.02.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

