Radiofrequency Ablation versus Cryoablation in the Treatment of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 29805800
- PMCID: PMC5901816
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/6276241
Radiofrequency Ablation versus Cryoablation in the Treatment of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary vein isolation is commonly performed using radiofrequency energy with cryoablation gaining acceptance. We performed a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials which compared radiofrequency versus cryoablation for patients with atrial fibrillation.
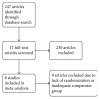
Methods: A systematic search strategy identified both published and unpublished articles from inception to November 10, 2016, in multiple databases. The primary outcomes for this meta-analysis were long-term freedom from atrial fibrillation at 12-month follow-up and overall postoperative complication rates. For all included studies, the methodological quality was assessed through the Cochrane Collaboration's tool for risk of bias.
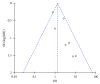
Results: A total of 247 articles were identified with eight being included in this review as they satisfied the prespecified inclusion criteria. Overall, there was no significant difference in freedom from atrial fibrillation at ≥12-month follow-up between those receiving cryoballoon and radiofrequency ablation, respectively (OR = 0.98, CI = 0.67-1.43, I2 = 56%, p=0.90). Additionally, the secondary outcomes of duration of ablation, fluoroscopy time, and ablation time failed to reach significance. Cryoballoon ablation had significantly greater odds of postoperative phrenic nerve injury at 12-month follow-up.
Conclusions: Our meta-analysis suggests that cryoballoon ablation provides comparable benefits with regard to freedom from atrial fibrillation at medium-term follow-up, fluoroscopy time, ablation time, operative duration, and overall complication rate in comparison to radiofrequency ablation.
Figures







References
-
- Skelly A., Hashimoto R., Al-Khatib S., et al. Catheter Ablation for Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation. Rockville, MD, USA: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2015. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK305760. - PubMed
-
- Luik A., Radzewitz A., Kieser M., et al. Cryoballoon versus open irrigated radiofrequency ablation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: the prospective, randomized, controlled, noninferiority freeze AF study. Circulation. 2015;132(14):1311–1319. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.115.016871. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
