Endoscopic versus Open Bursectomy for Prepatellar and Olecranon Bursitis
- PMID: 29805943
- PMCID: PMC5969792
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2374
Endoscopic versus Open Bursectomy for Prepatellar and Olecranon Bursitis
Abstract
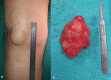
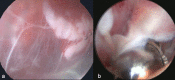
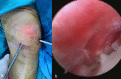
Objectives Bursitis of the olecranon and the patella are not rare disorders, and conservative management is successful in most cases. However, when patients do not respond to conservative treatment, open excisional surgery or, recently, endoscopic bursectomy, can be used. The aim of this study was to evaluate the results of open and endoscopic treatments of olecranon and prepatellar bursitis. Patients and methods Forty-nine patients (37 male and 12 female), who were treated with endoscopic bursectomy (25 patients) or open bursectomy (24 patients) were included in this study. Thirty patients had olecranon bursitis, while 19 patients had prepatellar bursitis. The patients' average age was 61.1 ± 12.3 (range 33-81) years. All of the patients' hospitalization and surgery times were recorded. The satisfaction of the patients was evaluated with a satisfaction scoring system, as well as by evaluating residual pain, the range of joint movement, and the cosmetic results of the procedure. Results The average follow-up time was 16 ± 9 months (range 12-27). The median operation time was 23.2 ± 3.5 minutes for the endoscopic bursectomy group and 26.4 ± 6.8 minutes for the open bursectomy group. The median hospitalization time was 0.56 ± 0.5 days (range 0-1 day) for the endoscopic group and 1 ± 0 days for the open bursectomy group (P<0.01). According to the patient satisfaction questionnaire, the endoscopic bursectomy group's score was 8.5 ± 1.3 (range 5-10), and the open bursectomy group's score was 5.29 ± 1.8 (range 1-9) (P<0.01). Conclusion Endoscopic bursectomy is a time-saving and efficient surgical treatment option for patients with prepatellar and olecranon bursitis.
Keywords: bursitis; elbow arthroscopy; endoscopic; endoscopic bursectomy; knee arthroscopy; minimally invasive surgery; olecranon bursitis; open bursectomy; prepatellar bursitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Surgical Outcomes in Endoscopic Versus Open Bursectomy of the Septic Prepatellar or Olecranon Bursa.Orthopedics. 2019 Jul 1;42(4):e381-e384. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20190321-04. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Orthopedics. 2019. PMID: 30913297
-
Management of septic and aseptic prepatellar bursitis: a systematic review.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022 Oct;142(10):2445-2457. doi: 10.1007/s00402-021-03853-9. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022. PMID: 33721054
-
No Wound Healing Complications or Recurrences Were Seen and a High Level of Satisfaction Was Reported in Patients Who Underwent Endoscopic Olecranon Bursectomy for Recalcitrant Olecranon Bursitis.Arthrosc Sports Med Rehabil. 2024 Jan 17;6(1):100832. doi: 10.1016/j.asmr.2023.100832. eCollection 2024 Feb. Arthrosc Sports Med Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38299046 Free PMC article.
-
Prepatellar and olecranon arthroscopic bursectomy.Clin Sports Med. 1993 Jan;12(1):137-42. Clin Sports Med. 1993. PMID: 8418974
-
Treatment and outcome with traumatic lesions of the olecranon and prepatellar bursa: a literature review apropos a retrospective analysis including 552 cases.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017 Jun;137(6):823-827. doi: 10.1007/s00402-017-2690-2. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017. PMID: 28447166 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation and Management of Hand, Wrist and Elbow Injuries in Ice Hockey.Open Access J Sports Med. 2020 Apr 28;11:93-103. doi: 10.2147/OAJSM.S246414. eCollection 2020. Open Access J Sports Med. 2020. PMID: 32425621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory arthritis and the elbow surgeon.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021 Jul 1;20:101492. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2021.101492. eCollection 2021 Sep. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021. PMID: 34277343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surgical Management of a Large Chronic Prepatellar Bursitis: 2-Stage Technique.Case Rep Orthop. 2020 Jan 13;2020:3204014. doi: 10.1155/2020/3204014. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Orthop. 2020. PMID: 32395360 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic resection of tendon xanthoma in the elbow of a patient with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis.BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Nov 12;14(11):e244931. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-244931. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34772677 Free PMC article.
-
Intrabursal Doxycycline Sclerotherapy for Recurrent Olecranon Bursitis of the Elbow: A Case Control Study.J Hand Surg Glob Online. 2024 Apr 8;6(4):504-509. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsg.2024.03.006. eCollection 2024 Jul. J Hand Surg Glob Online. 2024. PMID: 39166200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lower extremity bursitis. Butcher JD, Salzman KL, Lillegard WA. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/8638508. Am Fam Physician. 1996;53:2317–2324. - PubMed
-
- Complications following resection of the olecranon bursa. Degreef I, Smet LD. https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/1bf2/4e4148956f3908c0583e0c186940ca3ebe.... Acta Orthop Belg. 2006;72:400–403. - PubMed
-
- Endoscopic bursectomy for the treatment of septic pre-patellar bursitis: a case series. Dillon JP. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132:921–925. - PubMed
-
- Patella tendon rupture after arthroscopic resection of the prepatellar bursa: a case report. Epstein DM, Capeci CM, Rokito A. http://presentationgrafix.com/_dev/cake/files/archive/pdfs/260.pdf. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2010;68:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Treatment of nonseptic olecranon bursitis: a controlled, blinded prospective trial. Smith DL. Arch Intern Med. 1989;149:2527–2530. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
