Overcoming Ovarian Cancer Drug Resistance with a Cold Responsive Nanomaterial
- PMID: 29806003
- PMCID: PMC5968444
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.8b00050
Overcoming Ovarian Cancer Drug Resistance with a Cold Responsive Nanomaterial
Erratum in
-
Correction to Overcoming Ovarian Cancer Drug Resistance with a Cold Responsive Nanomaterial.ACS Cent Sci. 2021 May 26;7(5):909. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.1c00530. Epub 2021 May 17. ACS Cent Sci. 2021. PMID: 34079906 Free PMC article.
Retraction in
-
Retraction of "Overcoming Ovarian Cancer Drug Resistance with a Cold Responsive Nanomaterial".ACS Cent Sci. 2023 Apr 11;9(4):844. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.3c00335. eCollection 2023 Apr 26. ACS Cent Sci. 2023. PMID: 37122466 Free PMC article.
Abstract
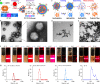
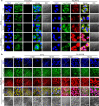
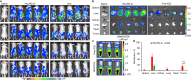
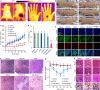
Drug resistance due to overexpression of membrane transporters in cancer cells and the existence of cancer stem cells (CSCs) is a major hurdle to effective and safe cancer chemotherapy. Nanoparticles have been explored to overcome cancer drug resistance. However, drug slowly released from nanoparticles can still be efficiently pumped out of drug-resistant cells. Here, a hybrid nanoparticle of phospholipid and polymers is developed to achieve cold-triggered burst release of encapsulated drug. With ice cooling to below ∼12 °C for both burst drug release and reduced membrane transporter activity, binding of the drug with its target in drug-resistant cells is evident, while it is minimal in the cells kept at 37 °C. Moreover, targeted drug delivery with the cold-responsive nanoparticles in combination with ice cooling not only can effectively kill drug-resistant ovarian cancer cells and their CSCs in vitro but also destroy both subcutaneous and orthotopic ovarian tumors in vivo with no evident systemic toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): The views reported in this paper do not reflect the views of the Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government. CMJ has an equity position in Cellth LLC. All other authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Rubbia-Brandt L.; Audard V.; Sartoretti P.; Roth A.; Brezault C.; Le Charpentier M.; Dousset B.; Morel P.; Soubrane O.; Chaussade S. Severe hepatic sinusoidal obstruction associated with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 460–466. 10.1093/annonc/mdh095. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

