[Photoelectric guided navigation unilateral puncture of the percutaneous kyphoplasty in treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture]
- PMID: 29806413
- PMCID: PMC8414082
- DOI: 10.7507/1002-1892.201709115
[Photoelectric guided navigation unilateral puncture of the percutaneous kyphoplasty in treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture]
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the safety of photoelectric guided navigation unilateral puncture of the percutaneous kyphoplasty (PKP) in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture (OVCF).
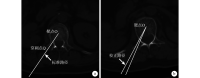
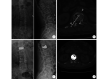
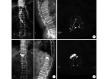
Methods: A randomized controlled clinical research was performed between June 2015 and January 2017. Eighty-five cases of OVCF were treated with photoelectric guided navigation unilateral puncture of the PKP (trial group, 43 cases) or C arm fluoroscopy unilateral puncture of the PKP (control group, 42 cases) respectively. There was no significant difference in gender, age, disease duration, segmental fracture, AO classification, bone mineral density, and preoperative visual analogue scale (VAS) score between 2 groups ( P>0.05). The concordance rate of puncture path and design path, the incidence of pedicle wall breaking, the incidence of bone cement leakage, and the rate of bone cement distribution center were observed and calculated on postoperative CT images; the intraoperative X-ray exposure frequency, frequency of puncture, operation time, VAS scores before operation and at 2 days after operation, and postoperative blood vessel or nerve injury were recorded and compared.
Results: The intraoperative X-ray exposure frequency and puncture frequency in trial group were significantly less than those in control group ( P<0.05), but there was no significant difference in operation time between 2 groups ( t=0.440, P=0.661). The VAS scores of 2 groups at 2 days after operation were significantly improved when compared with preoperative ones ( P<0.05), but there was no significant difference in VAS score at 2 days after operation between 2 groups ( t=0.406, P=0.685). All the patients were followed up 6-18 months (mean, 10 months). No blood vessel or nerve injury occurred in 2 groups. The incidence of pedicle wall breaking, the incidence of bone cement leakage, the concordance rate of puncture path and design path, and the rate of bone cement distribution center in trial group were 2.33% (1/43), 2.33% (1/43), 86.05% (37/43), and 88.37% (38/43) respectively, all showing significant differences when compared with those of control group [19.05% (8/42), 21.43% (9/42), 45.24% (19/42), and 50.00% (21/42) respectively] ( P<0.05).
Conclusion: Intraoperative photoelectric guided navigation unilateral puncture of the PKP can improve the success rate of target puncture and reduce the incidence of pedicle wall breaking effectively, and achieve better bone cement distribution and better security.
目的: 评估光电导航下个体化单侧穿刺椎体后凸成形术(percutaneous kyphoplasty,PKP)治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折(osteoporosis vertebral compression fracture,OVCF)的安全性。.
方法: 2015 年 6 月—2017 年 1 月,采用随机对照研究方法,对收治的 85 例 OVCF 患者分别采用光电导航引导下个体化单侧穿刺方法(观察组 43 例)或常规 C 臂 X 线机透视下单侧穿刺方法(对照组 42 例)行 PKP 治疗。两组患者性别、年龄、病程、累及节段、骨折 AO 分型、骨密度等级及术前疼痛视觉模拟评分(VAS)等一般资料比较差异无统计学意义( P>0.05)。术后 CT 横断面图像上观察并计算穿刺路径与设计路径的吻合率、椎弓根内壁突破率、骨水泥渗漏率和骨水泥中心分布率;记录两组患者术中 X 线暴露次数、穿刺次数、手术时间、术前和术后 2 d VAS 评分及术后血管、神经损伤等相关并发症发生情况。.
结果: 观察组术中 X 线暴露次数及穿刺次数明显少于对照组( P<0.05),但两组手术时间比较差异无统计学意义( t=0.440, P=0.661)。术后 2 d 两组 VAS 评分均较术前显著改善( P<0.05);但术后 2 d 两组间比较差异无统计学意义( t=0.406, P=0.685)。两组患者均获随访,随访时间 6~18 个月,平均 10 个月。两组均无血管、神经损伤等相关并发症发生。术后 48 h 观察组椎弓根内壁突破率、骨水泥渗漏率、穿刺路径吻合率和骨水泥中心分布率分别为 2.33%(1/43)、2.33%(1/43)、86.05%(37/43)、88.37%(38/43),与对照组[分别为 19.05%(8/42)、21.43%(9/42)、45.24%(19/42)、50.00%(21/42)]比较差异均有统计学意义( P<0.05)。.
结论: 术中光电导航下个体化单侧穿刺 PKP 能提高靶点穿刺成功率,有效减少椎弓根内壁穿破,能够获得更好的骨水泥分布,具有更高的安全性。.
Keywords: Percutaneous kyphoplasty; cement distribution; osteoporosis vertebral compression fractures; photoelectric navigation; puncture.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Robot-guided percutaneous kyphoplasty in treatment of multi-segmental osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Sep 15;34(9):1136-1141. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202002131. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32929907 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Bilateral percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty through unilateral transverse process-extrapedicular approach for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture of lumbar].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Aug 15;35(8):1007-1013. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202103028. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34387430 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[A prospective study of vertebroplasty with reverse designed unilateral targeted puncture for osteoporotic thoracolumbar compression fractures].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Nov 15;36(11):1400-1406. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202206063. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36382459 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Comparison of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Balloon Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Single Level Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Meta-analysis of the Literature.Pain Physician. 2015 May-Jun;18(3):209-22. Pain Physician. 2015. PMID: 26000665 Review.
-
Effect of percutaneous vertebroplasty versus percutaneous kyphoplasty on post-operative wound pain in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Int Wound J. 2024 Mar;21(3):e14745. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14745. Int Wound J. 2024. Retraction in: Int Wound J. 2025 Apr;22(4):e70404. doi: 10.1111/iwj.70404. PMID: 38484743 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
Percutaneous vertebroplasty with granulated allogeneic bone grafting using screw-view model of navigation for thoracolumbar compressive fracture: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 May;98(20):e15715. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015715. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31096524 Free PMC article.
-
EFFECT OF PKP ON SERUM SOST IN PATIENTS WITH VERTEaBRAL COMPRESSION FRACTURES.Acta Ortop Bras. 2020 Nov-Dec;28(6):323-326. doi: 10.1590/1413-785220202806228603. Acta Ortop Bras. 2020. PMID: 33328791 Free PMC article.
-
A novel computer navigation model guided unilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty for vertebral compression fracture: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Oct 30;99(44):e22468. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022468. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33126302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang H, Liu H, Wang S, et al Review of Percutaneous Kyphoplasty in China. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2016;41 Suppl 19:B52–58. - PubMed
-
- Lamy O, Uebelhart B, Aubry-Rozier B Risks and benefits of percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty in the management of osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25(3):807–819. - PubMed
-
- 刘小勇, 杨惠林, 唐天驷, 等 椎体后凸成形术棘突定位穿刺点与穿刺轨道的研究. 中华骨科杂志. 2005;25(8):462–466.
-
- Wang S, Wang Q, Kang J, et al An imaging anatomical study on percutaneous kyphoplasty for lumbar via a unilateral transverse process-pedicle approach. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2014;39(9):701–706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
