It's not magic - Hsp90 and its effects on genetic and epigenetic variation
- PMID: 29807130
- PMCID: PMC6281791
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.05.015
It's not magic - Hsp90 and its effects on genetic and epigenetic variation
Abstract
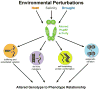
Canalization, or phenotypic robustness in the face of environmental and genetic perturbation, is an emergent property of living systems. Although this phenomenon has long been recognized, its molecular underpinnings have remained enigmatic until recently. Here, we review the contributions of the molecular chaperone Hsp90, a protein that facilitates the folding of many key regulators of growth and development, to canalization of phenotype - and de-canalization in times of stress - drawing on studies in eukaryotes as diverse as baker's yeast, mouse ear cress, and blind Mexican cavefish. Hsp90 is a hub of hubs that interacts with many so-called 'client proteins,' which affect virtually every aspect of cell signaling and physiology. As Hsp90 facilitates client folding and stability, it can epistatically suppress or enable the expression of genetic variants in its clients and other proteins that acquire client status through mutation. Hsp90's vast interaction network explains the breadth of its phenotypic reach, including Hsp90-dependent de novo mutations and epigenetic effects on gene regulation. Intrinsic links between environmental stress and Hsp90 function thus endow living systems with phenotypic plasticity in fluctuating environments. As environmental perturbations alter Hsp90 function, they also alter Hsp90's interaction with its client proteins, thereby re-wiring networks that determine the genotype-to-phenotype map. Ensuing de-canalization of phenotype creates phenotypic diversity that is not simply stochastic, but often has an underlying genetic basis. Thus, extreme phenotypes can be selected, and assimilated so that they no longer require environmental stress to manifest. In addition to acting on standing genetic variation, Hsp90 perturbation has also been linked to increased frequency of de novo variation and several epigenetic phenomena, all with the potential to generate heritable phenotypic change. Here, we aim to clarify and discuss the multiple means by which Hsp90 can affect phenotype and possibly evolutionary change, and identify their underlying common feature: at its core, Hsp90 interacts epistatically through its chaperone function with many other genes and their gene products. Its influence on phenotypic diversification is thus not magic but rather a fundamental property of genetics.
Keywords: Buffering; Canalization; Capacitor; Hsp90; Potentiate; Robustness.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


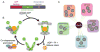


References
-
- Felix MA, Wagner A. Robustness and evolution: concepts, insights and challenges from a developmental model system. Heredity (Edinb) 2008;100(2):132–40. - PubMed
-
- Bergman A, Siegal ML. Evolutionary capacitance as a general feature of complex gene networks. Nature. 2003;424(6948):549–52. - PubMed
-
- de Visser JA, Hermisson J, Wagner GP, Ancel Meyers L, Bagheri-Chaichian H, Blanchard JL, Chao L, Cheverud JM, Elena SF, Fontana W, Gibson G, Hansen TF, Krakauer D, Lewontin RC, Ofria C, Rice SH, von Dassow G, Wagner A, Whitlock MC. Perspective: Evolution and detection of genetic robustness. Evolution Int J Org Evolution. 2003;57(9):1959–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

