Selective Insulin-like Growth Factor Resistance Associated with Heart Hemorrhages and Poor Prognosis in a Novel Preclinical Model of the Hematopoietic Acute Radiation Syndrome
- PMID: 29809108
- PMCID: PMC6118398
- DOI: 10.1667/RR14993.1
Selective Insulin-like Growth Factor Resistance Associated with Heart Hemorrhages and Poor Prognosis in a Novel Preclinical Model of the Hematopoietic Acute Radiation Syndrome
Abstract
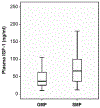
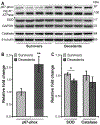
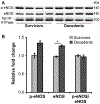
Although bone marrow aplasia has been considered for the past decades as the major contributor of radiation-induced blood disorders, cytopenias alone are insufficient to explain differences in the prevalence of bleeding. In this study, the minipig was used as a novel preclinical model of hematopoietic acute radiation syndrome to assess if factors other than platelet counts correlated with bleeding and survival. We sought to determine whether radiation affected the insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) pathway, a growth hormone with cardiovascular and radioprotective features. Gottingen and Sinclair minipigs were exposed to ionizing radiation at hematopoietic doses. The smaller Gottingen minipig strain was more sensitive to radiation; differences in IGF-1 levels were minimal, suggesting that increased sensitivity could depend on weak response to the hormone. Radiation caused IGF-1 selective resistance by inhibiting the anti-inflammatory anti-oxidative stress IRS/PI3K/Akt but not the pro-inflammatory MAPK kinase pathway, shifting IGF-1 signaling towards a pro-oxidant, pro-inflammatory environment. Selective IGF-1 resistance associated with hemorrhages in the heart, poor prognosis, increase in C-reactive protein and NADPH oxidase 2, uncoupling of endothelial nitric oxide synthase, inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) synthesis and imbalance between the vasodilator NO and the vasoconstrictor endothelin-1 molecules. Selective IGF-1 resistance is a novel mechanism of radiation injury, associated with a vicious cycle amplifying reactive oxygen species-induced damage, inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. In the presence of thrombocytopenia, selective inhibition of IGF-1 cardioprotective function may contribute to the development of hemostatic disorders. This finding may be particularly relevant for individuals with low IGF-1 activity, such as the elderly or those with cardiometabolic dysfunctions.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dysregulated Cardiac IGF-1 Signaling and Antioxidant Response Are Associated with Radiation Sensitivity.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 17;21(14):5049. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145049. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32708958 Free PMC article.
-
Neulasta Regimen for the Hematopoietic Acute Radiation Syndrome: Effects Beyond Neutrophil Recovery.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019 Mar 15;103(4):935-944. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.11.043. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019. PMID: 30496878
-
Investigating the Multifaceted Nature of Radiation-Induced Coagulopathies in a Göttingen Minipig Model of Hematopoietic Acute Radiation Syndrome.Radiat Res. 2021 Aug 1;196(2):156-174. doi: 10.1667/RADE-20-00073.1. Radiat Res. 2021. PMID: 34019667
-
Endothelial dysfunction, endothelial nitric oxide bioavailability, tetrahydrobiopterin, and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate in cardiovascular disease. Where are we with therapy?Microvasc Res. 2018 Sep;119:7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2018.03.012. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Microvasc Res. 2018. PMID: 29596860 Review.
-
Endothelial Dysfunction in Obesity and Therapeutic Targets.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:489-538. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39287863 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative Stress in Radiation-Induced Cardiotoxicity.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Mar 1;2020:3579143. doi: 10.1155/2020/3579143. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32190171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Late Health Effects of Partial Body Irradiation Injury in a Minipig Model Are Associated with Changes in Systemic and Cardiac IGF-1 Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 23;22(6):3286. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063286. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33807089 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated Cardiac IGF-1 Signaling and Antioxidant Response Are Associated with Radiation Sensitivity.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 17;21(14):5049. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145049. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32708958 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Expression Profiles from Heart, Lung and Liver Samples of Total-Body-Irradiated Minipigs: Implications for Predicting Radiation-Induced Tissue Toxicity.Radiat Res. 2020 Oct 2;194(4):411-430. doi: 10.1667/RADE-20-00123.1. Radiat Res. 2020. PMID: 32936898 Free PMC article.
-
Early to sustained impacts of lethal radiation on circulating miRNAs in a minipig model.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 28;13(1):18496. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45250-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37898651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mandel L, Travnícek J, Talafantova M, Zahradníckova M. The LD50/30 and the survival time in whole-body gamma-irradiated conventional and germfree Minnesota miniature piglets. Z Versuchstierkd 1980; 22:96–100. - PubMed
-
- Moroni M, Coolbaugh TV, Lombardini E, Mitchell JM, Moccia KD, Shelton LJ, et al. Hematopoietic radiation syndrome in the Göttingen minipig. Radiat Res 2011; 176:89–101. - PubMed
-
- Simianer H, Kohn F. Genetic management of the Gottingen minipig population. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 2010; 62:2216–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

