A Central Extended Amygdala Circuit That Modulates Anxiety
- PMID: 29844022
- PMCID: PMC6001032
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0705-18.2018
A Central Extended Amygdala Circuit That Modulates Anxiety
Abstract
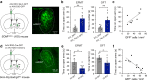
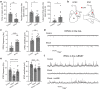
Both the amygdala and the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) have been implicated in maladaptive anxiety characteristics of anxiety disorders. However, the underlying circuit and cellular mechanisms have remained elusive. Here we show that mice with Erbb4 gene deficiency in somatostatin-expressing (SOM+) neurons exhibit heightened anxiety as measured in the elevated plus maze test and the open field test, two assays commonly used to assess anxiety-related behaviors in rodents. Using a combination of electrophysiological, molecular, genetic, and pharmacological techniques, we demonstrate that the abnormal anxiety in the mutant mice is caused by enhanced excitatory synaptic inputs onto SOM+ neurons in the central amygdala (CeA), and the resulting reduction in inhibition onto downstream SOM+ neurons in the BNST. Notably, our results indicate that an increase in dynorphin signaling in SOM+ CeA neurons mediates the paradoxical reduction in inhibition onto SOM+ BNST neurons, and that the consequent enhanced activity of SOM+ BNST neurons is both necessary for and sufficient to drive the elevated anxiety. Finally, we show that the elevated anxiety and the associated synaptic dysfunctions and increased dynorphin signaling in the CeA-BNST circuit of the Erbb4 mutant mice can be recapitulated by stress in wild-type mice. Together, our results unravel previously unknown circuit and cellular processes in the central extended amygdala that can cause maladaptive anxiety.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT The central extended amygdala has been implicated in anxiety-related behaviors, but the underlying mechanisms are unclear. Here we found that somatostatin-expressing neurons in the central amygdala (CeA) controls anxiety through modulation of the stria terminalis, a process that is mediated by an increase in dynorphin signaling in the CeA. Our results reveal circuit and cellular dysfunctions that may account for maladaptive anxiety.
Keywords: BNST; ErbB4; anxiety; central amygdala; dynorphin; stress.
Copyright © 2018 the authors 0270-6474/18/385567-17$15.00/0.
Figures
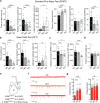

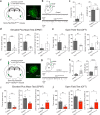
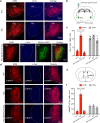

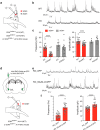

Comment in
-
Insights into the Neurobiology of Anxiety and a Potential Target for Pharmacotherapy.J Neurosci. 2018 Oct 17;38(42):8919-8921. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1461-18.2018. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30333184 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Al-Hasani R, McCall JG, Shin G, Gomez AM, Schmitz GP, Bernardi JM, Pyo CO, Park SI, Marcinkiewcz CM, Crowley NA, Krashes MJ, Lowell BB, Kash TL, Rogers JA, Bruchas MR (2015) Distinct subpopulations of nucleus accumbens dynorphin neurons drive aversion and reward. Neuron 87:1063–1077. 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.08.019 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
