Whole-Genome Sequencing in Cancer
- PMID: 29844223
- PMCID: PMC6396343
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a034579
Whole-Genome Sequencing in Cancer
Abstract
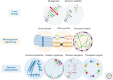
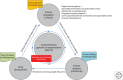
Genome sequencing of cancer has fundamentally advanced our understanding of the underlying biology of this disease, and more recently has provided approaches to characterize and monitor tumors in the clinic, guiding and evaluating treatment. Although cancer research is relying more on whole-genome characterization, the clinical application of genomics is largely limited to targeted sequencing approaches, tailored to capture specific clinically relevant biomarkers. However, as sequencing costs reduce, and the tools to effectively analyze complex and large-scale data improve, the ability to effectively characterize whole genomes at scale in a clinically relevant time frame is now being piloted. This ability effectively blurs the line between clinical cancer research and the clinical management of the disease. This leads to a new paradigm in cancer management in which real-time analysis of an individual's disease can have a rapid and lasting impact on our understanding of how clinical practices need to change to exploit novel therapeutic rationales. In this article, we will discuss how whole-genome sequencing (WGS), often combined with transcriptome analysis, has been used to understand cancer and how this approach is uniquely positioned to provide a comprehensive view of an evolving disease in response to therapy.
Copyright © 2019 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
