Alleviation of Acute Lung Injury in Rats with Sepsis by Resveratrol via the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Nuclear Factor-Erythroid 2 Related Factor 2/Heme Oxygenase-1 (PI3K/Nrf2/HO-1) Pathway
- PMID: 29844304
- PMCID: PMC6004080
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.910245
Alleviation of Acute Lung Injury in Rats with Sepsis by Resveratrol via the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Nuclear Factor-Erythroid 2 Related Factor 2/Heme Oxygenase-1 (PI3K/Nrf2/HO-1) Pathway
Abstract
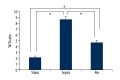
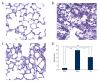
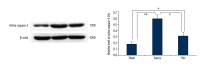
BACKGROUND Resveratrol (Res) is a type of polyphenol found in many plants, which can protect important organs from the damage induced by sepsis. However, the exact mechanism of its protective effect has not been established. This study investigated the effect of Res on the PI3K/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in rats with sepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI). MATERIAL AND METHODS Male Wistar rats were treated with 30 mg/kg Res by intraperitoneal administration for 1 hour immediately after cecal ligation and puncture. Levels of MIP-2, IL-18, and IL-10 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were determined. Lung tissues were collected to measure the wet-to-dry (W/D) ratios, oxidative stress index, and lung injury scores. Expression levels of Akt, p-Akt, HO-1, Nrf-2, and active caspase-3 proteins were determined by western blotting; expression of HO-1 mRNA was determined by RT-PCR. RESULTS Treatment with Res significantly decreased the levels of MIP-2 and IL-18 and increased IL-10 in the BALF of rats with sepsis-induced ALI. In addition, Res also effectively reduced the W/D lung weight ratio, lung injury score, and the levels of MDA (malondialdehyde) and 8-OHdG. Conversely, Res increased SOD (superoxide dismutase) activity in the lung tissue. Moreover, Res significantly induced higher HO-1 mRNA expression, upregulated HO-1 and Nrf-2 protein expression, and the phosphorylation of Akt in the lung tissue. In contrast, the levels of activated caspase-3 protein were decreased in Res-treated rats (P<0.05). CONCLUSIONS Res could inhibit inflammation, oxidative stress, and cell apoptosis to alleviate ALI in septic rats through the inhibition of the PI3K/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Resveratrol Attenuates the Cytotoxicity Induced by Amyloid-β1-42 in PC12 Cells by Upregulating Heme Oxygenase-1 via the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2018 Feb;43(2):297-305. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2421-7. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 29090409
-
[Effect of SIRT1 regulating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway on sepsis-induced acute lung injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Mar;35(3):244-249. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220815-00745. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 36916335 Chinese.
-
Songorine inhibits oxidative stress-related inflammation through PI3K/AKT/NRF2 signaling pathway to alleviate lipopolysaccharide-induced septic acute lung injury.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2024 Apr;46(2):152-160. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2023.2281902. Epub 2023 Nov 17. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2024. PMID: 37977206
-
Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide: novel therapeutic strategies in critical care medicine.Curr Drug Targets. 2010 Dec;11(12):1485-94. doi: 10.2174/1389450111009011485. Curr Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20704552 Review.
-
New Insights into the Nrf-2/HO-1 Signaling Axis and Its Application in Pediatric Respiratory Diseases.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Nov 19;2019:3214196. doi: 10.1155/2019/3214196. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31827672 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resveratrol decreases CD45+ CD206- subtype macrophages in LPS-induced murine acute lung injury by SOCS3 signalling pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Dec;23(12):8101-8113. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14680. Epub 2019 Sep 27. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31559687 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Hesperidin Against Sepsis-Induced Lung Injury by Inducing the Heat-Stable Protein 70 (Hsp70)/Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4)/ Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response 88 (MyD88) Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Jan 4;25:107-114. doi: 10.12659/MSM.912490. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 30608918 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol as an Adjunctive Therapy for Excessive Oxidative Stress in Aging COVID-19 Patients.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Sep 9;10(9):1440. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091440. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrf2/PHB2 alleviates mitochondrial damage and protects against Staphylococcus aureus-induced acute lung injury.MedComm (2020). 2023 Dec 7;4(6):e448. doi: 10.1002/mco2.448. eCollection 2023 Dec. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 38077250 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Analysis of Pharmacology and Transcriptomics Predicts Resveratrol Will Ameliorate Microplastics-Induced Lung Damage by Targeting Ccl2 and Esr1.Toxics. 2024 Dec 14;12(12):910. doi: 10.3390/toxics12120910. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39771125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ornellas DS, Maron-Gutierrez T, Ornellas FM, et al. Early and late effects of bone marrow-derived mononuclear cell therapy on lung and distal organs in experimental sepsis. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011;178:304–14. - PubMed
-
- Eisenreich A, Raueh U. PI3K inhibitors in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Ther. 2011;29:29–36. - PubMed
-
- Motohashi H, Yamamoto M. Nrf2-Keapl defines a physiologically important stress response mechanism. Trends Mol Med. 2004;10:549–57. - PubMed
-
- Shen G, Jeong WS, Hu R, Kong AN. Regulation of Nrf2, NF-kappaB, and AP-1 signaling pathways by chemopreventive agents. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005;7:1648–63. - PubMed
-
- Cao TH, Jin SG, Fei DS, et al. Artesunate protects against sepsis-induced lung injury Via Heme Oxygenase-1 Modulation. Inflammation. 2016;39:651–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

