The Relationship between Serum Apelin Levels and the Severity of Calcific Aortic Stenosis
- PMID: 29844647
- PMCID: PMC5968342
- DOI: 10.6515/ACS.201805_34(3).20180207A
The Relationship between Serum Apelin Levels and the Severity of Calcific Aortic Stenosis
Abstract
Background: Apelin, an endogenous peptide, has recently gained attention due to its positive inotropic effects in heart failure physiopathology. We investigated the relationship between serum apelin levels and the severity of calcific aortic stenosis (AS).
Methods: A total of 68 consecutive patients diagnosed with calcific AS and a control group of 32 subjects were included in the study. The subjects were divided into three group as follows: the control group, the mild-moderate AS group and the severe AS group. Blood samples were obtained from all of the subjects, which were used for biochemical comparisons of apelin 36 and high-sensitive C-reactive protein (hsCRP) levels.
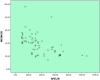
Results: Plasma apelin 36 levels were significantly lower in the patients with severe AS [490 (247-1074) pg/ml] compared to both the mild-moderate AS [209 (97-453) pg/ml] and control [660 (378-1200) pg/ml] groups (p < 0.001). Correlation analysis between the left ventricular mass index and apelin concentrations revealed a significant negative correlation between the two parameters (p < 0.001, r = -0.478).
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated decreased apelin levels and increased hsCRP concentrations in patients with severe calcific AS. Our findings may help to clarify the exact pathophysiologic role of apelin in cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: Aortic stenosis; Apelin; Apelin 36; Left ventricular hypertrophy.
Figures
References
-
- Tziomalos K, Athyros VG, Karagiannis A, Mikhailidis DP. Established and emerging vascular risk factors and the develop-ment of aortic stenosis: an opportunity for prevention? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008;12:809–820. - PubMed
-
- Dweck MR, Boon NA, Newby DE. Calcific aortic stenosis: a disease of the valve and the myocardium. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:1854–1863. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials