Role of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in the diagnosis and prognosis of patients with Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 29844807
- PMCID: PMC5958833
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6076
Role of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in the diagnosis and prognosis of patients with Parkinson's disease
Abstract
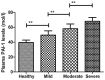
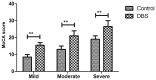
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disease that frequently results in memory disorders, cognitive decline and dementia. Previous studies have reported that plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) serves an important role in cardiovascular disease risk, adiposity, insulin resistance and inflammation. However, the role of PAI-1 in diagnosis and prognosis of patients with Parkinson's disease following deep brain stimulation (DBS) has not reported, to the best of our knowledge. Therefore, the purpose of the present study was to investigate the clinical significance of PAI-1 in patients with Parkinson's disease. Plasma PAI-1 levels were measured in 102 patients with Parkinson's disease who underwent DBS. It was demonstrated that plasma PAI-1 levels were significantly increased in patients with Parkinson's disease compared with healthy individuals (P<0.01). Patients with Parkinson's disease received DBS presented significantly improved cognitive competence compared with controls (P<0.01). DBS significantly decreased plasma PAI-1 levels in patients with Parkinson's disease compared with controls (P<0.05). It was also observed that plasma PAI-1 levels were significantly negatively associated with cognitive function for patients with Parkinson's disease (P<0.01). In conclusion, these findings demonstrated that the degree of Parkinson's disease severity is positively associated with circulating levels of plasma PAI-1 levels, which suggests that PAI-1 may be a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker for patients with Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; cognitive competence; deep brain stimulation; plasminogen activator inhibitor-1.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Association between plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to Parkinson's disease in Chinese patients.Acta Neurol Belg. 2022 Dec;122(6):1557-1566. doi: 10.1007/s13760-021-01843-7. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Acta Neurol Belg. 2022. PMID: 34845645
-
Serum Levels of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 in Patients with Parkinson's Disease.Med Princ Pract. 2024;33(6):562-568. doi: 10.1159/000540854. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Med Princ Pract. 2024. PMID: 39134015 Free PMC article.
-
Increased plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, decreased tissue factor pathway inhibitor, and unchanged thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor levels in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism.Eur J Endocrinol. 2009 May;160(5):863-8. doi: 10.1530/EJE-09-0069. Epub 2009 Feb 20. Eur J Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19233920
-
Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guideline on Subthalamic Nucleus and Globus Pallidus Internus Deep Brain Stimulation for the Treatment of Patients With Parkinson's Disease: Executive Summary.Neurosurgery. 2018 Jun 1;82(6):753-756. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyy037. Neurosurgery. 2018. PMID: 29538685 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrinolytic function and coronary risk.Curr Cardiol Rep. 1999 Jul;1(2):119-24. doi: 10.1007/s11886-999-0069-x. Curr Cardiol Rep. 1999. PMID: 10980830 Review.
Cited by
-
Exogenous Tetranectin Alleviates Pre-formed-fibrils-induced Synucleinopathies in SH-SY5Y Cells by Activating the Plasminogen Activation System.Neurochem Res. 2022 Oct;47(10):3192-3201. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03673-2. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 35895152
-
Elevated cerebrospinal fluid levels of SERPIN E1 in participants with lewy body diseases.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2025 Jun 13;11(1):166. doi: 10.1038/s41531-025-00984-3. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2025. PMID: 40514404 Free PMC article.
-
Plasminogen Activators in Neurovascular and Neurodegenerative Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 22;22(9):4380. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094380. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33922229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting NMDA Receptors at the Neurovascular Unit: Past and Future Treatments for Central Nervous System Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 7;23(18):10336. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810336. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the association between periodontitis and risk of Parkinson's disease: a nationwide retrospective cohort study.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 16;11(1):16594. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96147-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34400731 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
