Mycobacterial biomaterials and resources for researchers
- PMID: 29846561
- PMCID: PMC6251690
- DOI: 10.1093/femspd/fty042
Mycobacterial biomaterials and resources for researchers
Abstract
There are many resources available to mycobacterial researchers, including culture collections around the world that distribute biomaterials to the general scientific community, genomic and clinical databases, and powerful bioinformatics tools. However, many of these resources may be unknown to the research community. This review article aims to summarize and publicize many of these resources, thus strengthening the quality and reproducibility of mycobacterial research by providing the scientific community access to authenticated and quality-controlled biomaterials and a wealth of information, analytical tools and research opportunities.
Figures
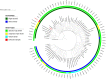
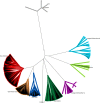
References
-
- Couvin D, Rastogi N. Tuberculosis - A global emergency: tools and methods to monitor, understand, and control the epidemic with specific example of the Beijing lineage. Tuberculosis 2015;95(Suppl 1):S177–89. - PubMed
-
- Couvin D, Zozio T, Rastogi N. SpolSimilaritySearch - A web tool to compare and search similarities between spoligotypes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Tuberculosis 2017;105:49–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

