Subcutaneous Fat Fibrosis Links Obesity to Insulin Resistance in Chinese Americans
- PMID: 29846621
- PMCID: PMC6126891
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2017-02301
Subcutaneous Fat Fibrosis Links Obesity to Insulin Resistance in Chinese Americans
Abstract
Objective: Type 2 diabetes presents at a lower body mass index (BMI) in Chinese individuals than in white individuals. We sought to determine the role of subcutaneous adipose tissue (SCAT)-intrinsic factors, vs BMI or adiposity per se, in the vulnerability of Chinese individuals to obesity-associated impairment of insulin sensitivity.
Research design and methods: Thirty-two Chinese and 30 white men and women from a cohort in the San Francisco Bay Area underwent anthropometric measurements, body composition (dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry) analyses, and measurement of fasting plasma glucose and insulin. Forty-eight also provided abdominal SCAT samples for transcriptional and biochemical analyses of tissue fibrosis.
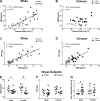
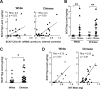
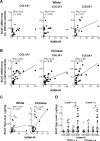
Results: BMI correlated with total body fat in white (r = 0.74, P < 0.001) but not Chinese individuals, whereas BMI correlated with visceral adipose tissue (VAT) accrual in both ethnicities (r = 0.88 and 0.81, respectively; P < 0.01). Insulin resistance (homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance) worsened with VAT mass, but not total body fat, in Chinese subjects (r = 0.63, P < 0.01), whereas it worsened with both in white individuals. By contrast, SCAT mRNA levels of genes encoding profibrotic proteins rose remarkably along with both BMI and VAT mass in Chinese but not white subjects. Similarly, SCAT levels of hydroxyproline, an indicator of tissue collagen content that correlated with increasing VAT mass, were higher in Chinese vs white subjects, particularly in the setting of relative insulin resistance.
Conclusions: Our findings dissociate BMI from adiposity in Chinese individuals and instead highlight SCAT fibrosis as a process linked to visceral adiposity and insulin resistance in this group.
Figures

References
-
- Gu D, He J, Duan X, Reynolds K, Wu X, Chen J, Huang G, Chen C-S, Whelton PK. Body weight and mortality among men and women in China. JAMA. 2006;295(7):776–783. - PubMed
-
- Zheng W, McLerran DF, Rolland B, Zhang X, Inoue M, Matsuo K, He J, Gupta PC, Ramadas K, Tsugane S, Irie F, Tamakoshi A, Gao Y-T, Wang R, Shu X-O, Tsuji I, Kuriyama S, Tanaka H, Satoh H, Chen C-J, Yuan J-M, Yoo K-Y, Ahsan H, Pan WH, Gu D, Pednekar MS, Sauvaget C, Sasazuki S, Sairenchi T, Yang G, Xiang Y-B, Nagai M, Suzuki T, Nishino Y, You S-L, Koh W-P, Park SK, Chen Y, Shen C-Y, Thornquist M, Feng Z, Kang D, Boffetta P, Potter JD. Association between body-mass index and risk of death in more than 1 million Asians. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(8):719–729. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deurenberg P, Yap M, van Staveren WA. Body mass index and percent body fat: a meta analysis among different ethnic groups. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1998;22(12):1164–1171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

