Ultrapotent Human Neutralizing Antibody Repertoires Against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus From a Recovered Patient
- PMID: 29846635
- PMCID: PMC7107445
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiy311
Ultrapotent Human Neutralizing Antibody Repertoires Against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus From a Recovered Patient
Abstract
Background: The Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) causes severe respiratory infection with a high (~35%) mortality rate. Neutralizing antibodies targeting the spike of MERS-CoV have been shown to be a therapeutic option for treatment of lethal disease.
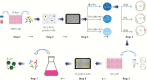
Methods: We describe the germline diversity and neutralizing activity of 13 potent human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that target the MERS-CoV spike (S) protein. Biological functions were assessed by live MERS-CoV, pseudotype particle and its variants, and structural basis was also determined by crystallographic analysis.
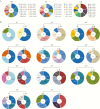
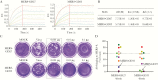
Results: Of the 13 mAbs displaying strong neutralizing activity against MERS-CoV, two with the immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable region (IGHV)1-69-derived heavy chain (named MERS-GD27 and MERS-GD33) showed the most potent neutralizing activity against pseudotyped and live MERS-CoV in vitro. Mutagenesis analysis suggested that MERS-GD27 and MERS-GD33 recognized distinct regions in S glycoproteins, and the combination of 2 mAbs demonstrated a synergistic effect in neutralization against pseudotyped MERS-CoV. The structural basis of MERS-GD27 neutralization and recognition revealed that its epitope almost completely overlapped with the receptor-binding site.
Conclusions: Our data provide new insights into the specific antibody repertoires and the molecular determinants of neutralization during natural MERS-CoV infection in humans. This finding supports additional efforts to design and develop novel therapies to combat MERS-CoV infections in humans.
Figures



References
-
- Zaki AM, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med 2012; 367:1814–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

