Effects of sucroferric oxyhydroxide and sevelamer carbonate on chronic kidney disease-mineral bone disorder parameters in dialysis patients
- PMID: 29846719
- PMCID: PMC6603395
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfy127
Effects of sucroferric oxyhydroxide and sevelamer carbonate on chronic kidney disease-mineral bone disorder parameters in dialysis patients
Abstract
Background: Treatment of hyperphosphataemia is the primary goal of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD) management. This post hoc analysis of a randomized, Phase 3 study evaluated the effects of 1-year treatment with the phosphate binders sucroferric oxyhydroxide or sevelamer carbonate ('sevelamer') on CKD-MBD indices among dialysis patients with hyperphosphataemia.
Methods: After a 2- to 4-week washout from previous phosphate binders, 1059 patients were randomized 2:1 to sucroferric oxyhydroxide 1.0-3.0 g/day (n = 710) or sevelamer 2.4-14.4 g/day (n = 349) for up to 24 weeks. Eligible patients enrolled in a 28-week extension. This post hoc analysis was performed for patients who completed ≥1 year of continuous treatment (n = 549). As the treatment groups showed similar CKD-MBD outcomes, the data were pooled for this analysis.
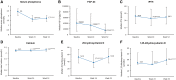
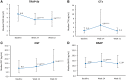
Results: Phosphate-binder therapy was associated with significant and sustained 30% reductions in serum phosphorus (P < 0.001). Median intact fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF-23) also significantly decreased (P < 0.001) by 64% over 1 year. Intact parathyroid hormone decreased significantly after 24 weeks (P < 0.001), but levels returned to near baseline values by Week 52; minimal changes in serum calcium were observed. Of the bone resorption markers evaluated, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5b (TRAP5b) decreased significantly (P < 0.001), whereas CTx increased transiently but returned to baseline levels by Week 52. The bone formation markers bone-specific alkaline phosphatase and osteocalcin both increased over 1 year of treatment.
Conclusions: Overall, 1 year of sucroferric oxyhydroxide or sevelamer treatment significantly reduced serum FGF-23, which has been associated with clinical benefit in patients with CKD. The trend towards increased bone formation marker levels indicates a beneficial effect on bone metabolism.
Keywords: bone markers; dialysis; hyperphosphataemia; phosphate binder; sucroferric oxyhydroxide.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures
References
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes CKD-MBD Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD). Kidney Int Suppl 2009; S1–S130 - PubMed
-
- Block GA, Klassen PS, Lazarus JM. et al. Mineral metabolism, mortality, and morbidity in maintenance hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2004; 15: 2208–2218 - PubMed
-
- Tentori F, Blayney MJ, Albert JM. et al. Mortality risk for dialysis patients with different levels of serum calcium, phosphorus, and PTH: the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). Am J Kidney Dis 2008; 52: 519–530 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

