Aqueous Humor Dynamics of the Brown-Norway Rat
- PMID: 29847660
- PMCID: PMC5967599
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.17-22915
Aqueous Humor Dynamics of the Brown-Norway Rat
Abstract
Purpose: The study aimed to provide a quantitative description of aqueous humor dynamics in healthy rat eyes.
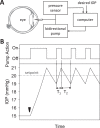
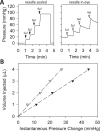
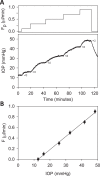
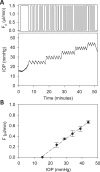
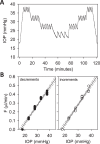
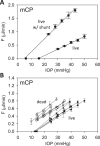
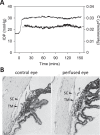
Methods: One eye of 26 anesthetized adult Brown-Norway rats was cannulated with a needle connected to a perfusion pump and pressure transducer. Pressure-flow data were measured in live and dead eyes by varying pump rate (constant-flow technique) or by modulating pump duty cycle to hold intraocular pressure (IOP) at set levels (modified constant-pressure technique). Data were fit by the Goldmann equation to estimate conventional outflow facility (C) and unconventional outflow rate (Fun). Parameter estimates were respectively checked by inserting a shunt of similar conductance into the eye and by varying eye hydration methodology.
Results: Rat IOP averaged 14.6 ± 1.9 mm Hg at rest. Pressure-flow data were repeatable and indistinguishable for the two perfusion techniques, yielding C = 0.023 ± 0.002 μL/min/mm Hg and Fun = 0.096 ± 0.024 μL/min. C was similar for live and dead eyes and increased upon shunt insertion by an amount equal to shunt conductance, validating measurement accuracy. At 100% humidity Fun dropped to 0.003 ± 0.030 μL/min. Physiological washout was not observed (-0.35 ± 0.65%/h), and trabecular anatomy looked normal.
Conclusions: Rat aqueous humor dynamics are intermediate in magnitude compared to those in mice and humans, consistent with species differences in eye size. C does not change with time or death. Evaporation complicates measurement of Fun even when eyes are not enucleated. Absence of washout is a notable finding seen only in mouse and human eyes to date.
Figures

References
-
- Bill A. . The aqueous humor drainage mechanism in the cynomolgus monkey (Macaca irus) with evidence for unconventional routes. . 1965; 4: 911– 919. - PubMed
-
- Bill A. . Conventional and uveo-scleral drainage of aqueous humour in the cynomolgus monkey (Macaca irus) at normal and high intraocular pressures. . 1966; 5: 45– 54. - PubMed
-
- Gong H, Tripathi RC, Tripathi BJ. . Morphology of the aqueous outflow pathway. . 1996; 33: 336– 367. - PubMed
-
- Tamm ER. . The trabecular meshwork outflow pathways: structural and functional aspects. . 2009; 88: 648– 655. - PubMed
-
- Alm A, Nilsson SF. . Uveoscleral outflow—a review. . 2009; 88: 760– 768. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

