Career Preferences and Perceptions of Cardiology Among US Internal Medicine Trainees: Factors Influencing Cardiology Career Choice
- PMID: 29847674
- PMCID: PMC6143073
- DOI: 10.1001/jamacardio.2018.1279
Career Preferences and Perceptions of Cardiology Among US Internal Medicine Trainees: Factors Influencing Cardiology Career Choice
Abstract
Importance: Few data exist on internal medicine trainees' selection of cardiology training, although this is important for meeting future cardiology workforce needs.
Objective: To discover trainees' professional development preferences and perceptions of cardiology, and their relationship to trainees' career choice.
Design, setting, and participants: We surveyed trainees to discover their professional development preferences and perceptions of cardiology and the influence of those perceptions and preferences on the trainees' career choices. Participants rated 38 professional development needs and 19 perceptions of cardiology. Data collection took place from February 2009, through January 2010. Data analysis was conducted from May 2017 to December 2017.
Main outcomes and measures: Multivariable models were used to determine the association of demographics and survey responses with prospective career choice.
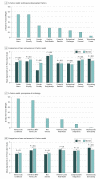
Results: A total of 4850 trainees were contacted, and 1123 trainees (of whom 625 [55.7%] were men) in 198 residency programs completed surveys (23.1% response; mean [SD] age, 29.4 [3.5] years). Principal component analysis of survey responses resulted in 8-factor and 6-factor models. Professional development preferences in descending order of significance were stable hours, family friendliness, female friendliness, the availability of positive role models, financial benefits, professional challenges, patient focus, and the opportunity to have a stimulating career. The top perceptions of cardiology in descending order of significance were adverse job conditions, interference with family life, and a lack of diversity. Women and future noncardiologists valued work-life balance more highly and had more negative perceptions of cardiology than men or future cardiologists, who emphasized the professional advantages available in cardiology. Professional development factors and cardiology perceptions were strongly associated with a decision to pursue or avoid a career in cardiology in both men and women.
Conclusions and relevance: Alignment of cardiology culture with trainees' preferences and perceptions may assist efforts to ensure the continued attractiveness of cardiology careers and increase the diversity of the cardiology workforce.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Choosing a Career in Cardiology: Where Are the Women?JAMA Cardiol. 2018 Aug 1;3(8):691-692. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2018.1286. JAMA Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29847614 No abstract available.
-
Role Models, Allies, and Diversity-Global Issues for Female Cardiology Trainees.JAMA Cardiol. 2018 Dec 1;3(12):1251-1252. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2018.3559. JAMA Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 30419109 No abstract available.
-
Role Models, Allies, and Diversity-Global Issues for Female Cardiology Trainees-Reply.JAMA Cardiol. 2018 Dec 1;3(12):1252. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2018.3570. JAMA Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 30419124 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

