Inhibition of Neuroinflammation by AIBP: Spinal Effects upon Facilitated Pain States
- PMID: 29847797
- PMCID: PMC6239868
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.04.110
Inhibition of Neuroinflammation by AIBP: Spinal Effects upon Facilitated Pain States
Abstract
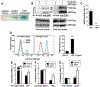
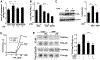
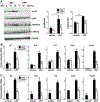
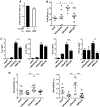
Apolipoprotein A-I binding protein (AIBP) reduces lipid raft abundance by augmenting the removal of excess cholesterol from the plasma membrane. Here, we report that AIBP prevents and reverses processes associated with neuroinflammatory-mediated spinal nociceptive processing. The mechanism involves AIBP binding to Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) and increased binding of AIBP to activated microglia, which mediates selective regulation of lipid rafts in inflammatory cells. AIBP-mediated lipid raft reductions downregulate LPS-induced TLR4 dimerization, inflammatory signaling, and expression of cytokines in microglia. In mice, intrathecal injections of AIBP reduce spinal myeloid cell lipid rafts, TLR4 dimerization, neuroinflammation, and glial activation. Intrathecal AIBP reverses established allodynia in mice in which pain states were induced by the chemotherapeutic cisplatin, intraplantar formalin, or intrathecal LPS, all of which are pro-nociceptive interventions known to be regulated by TLR4 signaling. These findings demonstrate a mechanism by which AIBP regulates neuroinflammation and suggest the therapeutic potential of AIBP in treating preexisting pain states.
Keywords: AIBP; TLR4; allodynia; chemotherapy; cholesterol; chronic pain; inflammation; lipid rafts; neuroinflammation; neuropathic pain.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests. Y.I.M. and T.L.Y. are inventors listed in patent applications related to the topic of this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Agalave NM, Larsson M, Abdelmoaty S, Su J, Baharpoor A, Lundback P, Palmblad K, Andersson U, Harris H, and Svensson CI (2014). Spinal HMGB1 induces TLR4-mediated long-lasting hypersensitivity and glial activation and regulates pain-like behavior in experimental arthritis. Pain 155, 1802–1813. - PubMed
-
- Blasi E, Barluzzi R, Bocchini V, Mazzolla R, and Bistoni F (1990). Immortalization of murine microglial cells by a v-raf/v-myc carrying retrovirus. J Neuroimmunol 27, 229–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

