Integrating Multimodal Radiation Therapy Data into i2b2
- PMID: 29847842
- PMCID: PMC5976493
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0038-1651497
Integrating Multimodal Radiation Therapy Data into i2b2
Abstract
Background: Clinical data warehouses are now widely used to foster clinical and translational research and the Informatics for Integrating Biology and the Bedside (i2b2) platform has become a de facto standard for storing clinical data in many projects. However, to design predictive models and assist in personalized treatment planning in cancer or radiation oncology, all available patient data need to be integrated into i2b2, including radiation therapy data that are currently not addressed in many existing i2b2 sites.
Objective: To use radiation therapy data in projects related to rectal cancer patients, we assessed the feasibility of integrating radiation oncology data into the i2b2 platform.
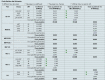
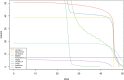
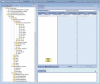
Methods: The Georges Pompidou European Hospital, a hospital from the Assistance Publique - Hôpitaux de Paris group, has developed an i2b2-based clinical data warehouse of various structured and unstructured clinical data for research since 2008. To store and reuse various radiation therapy data-dose details, activities scheduling, and dose-volume histogram (DVH) curves-in this repository, we first extracted raw data by using some reverse engineering techniques and a vendor's application programming interface. Then, we implemented a hybrid storage approach by combining the standard i2b2 "Entity-Attribute-Value" storage mechanism with a "JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) document-based" storage mechanism without modifying the i2b2 core tables. Validation was performed using (1) the Business Objects framework for replicating vendor's application screens showing dose details and activities scheduling data and (2) the R software for displaying the DVH curves.
Results: We developed a pipeline to integrate the radiation therapy data into the Georges Pompidou European Hospital i2b2 instance and evaluated it on a cohort of 262 patients. We were able to use the radiation therapy data on a preliminary use case by fetching the DVH curve data from the clinical data warehouse and displaying them in a R chart.
Conclusion: By adding radiation therapy data into the clinical data warehouse, we were able to analyze radiation therapy response in cancer patients and we have leveraged the i2b2 platform to store radiation therapy data, including detailed information such as the DVH to create new ontology-based modules that provides research investigators with a wider spectrum of clinical data.
Schattauer GmbH Stuttgart.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




References
-
- Degoulet P, Marin L, Lavril Met al.The HEGP component-based clinical information system Int J Med Inform 200369(2-3):115–126. - PubMed
-
- Zapletal E, Rodon N, Grabar N, Degoulet P.Methodology of integration of a clinical data warehouse with a clinical information system: the HEGP case Stud Health Technol Inform 2010160(Pt 1):193–197. - PubMed
-
- Jannot A-S, Zapletal E, Avillach P, Mamzer M-F, Burgun A, Degoulet P. The Georges Pompidou University Hospital Clinical Data Warehouse: a 8-years follow-up experience. Int J Med Inform. 2017;102:21–28. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

