Immunotherapeutic interventions of Triple Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 29848327
- PMCID: PMC5977468
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-018-1514-7
Immunotherapeutic interventions of Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
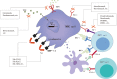
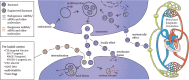
Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) is a highly heterogeneous subtype of breast cancer that lacks the expression of oestrogen receptors, progesterone receptors and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2. Although TNBC is sensitive to chemotherapy, the overall outcomes of TNBC are worse than for other breast cancers, and TNBC is still one of the most fatal diseases for women. With the discovery of antigens specifically expressed in TNBC cells and the developing technology of monoclonal antibodies, chimeric antigen receptors and cancer vaccines, immunotherapy is emerging as a novel promising option for TNBC. This review is mainly focused on the tumour microenvironment and host immunity, Triple Negative Breast Cancer and the clinical treatment of TNBC, novel therapies for cancer and immunotherapy for TNBC, and the future outlook for the treatment for TNBC and the interplay between the therapies, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors with targeted treatments in TNBC, adoptive cell therapy, cancer vaccines. The review also highlights recent reports on the synergistic effects of immunotherapy and chemotherapy, antibody-drug conjugates, and exosomes, as potential multifunctional therapeutic agents in TNBC.
Keywords: Antibody therapies; Chemotherapy; Exosome; Immunotherapy; Triple Negative Breast Cancer.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

