Anaplastic carcinoma of the pancreas diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 29848384
- PMCID: PMC5977485
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-018-1615-1
Anaplastic carcinoma of the pancreas diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Anaplastic carcinoma of the pancreas is a rare pancreatic neoplasm with a poor prognosis. It is classified as a variant of ductal adenocarcinoma, but the clinical features and treatment of it remain unknown because of its rarity and aggressiveness. Endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration are useful techniques for the diagnosis of pancreatic tumors with high sensitivity and specificity.
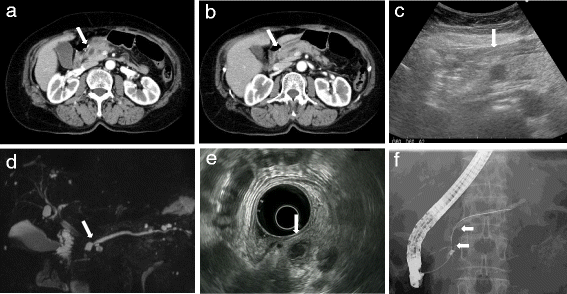
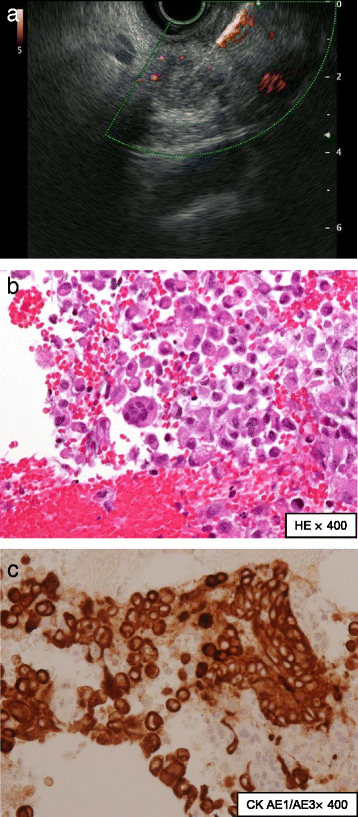
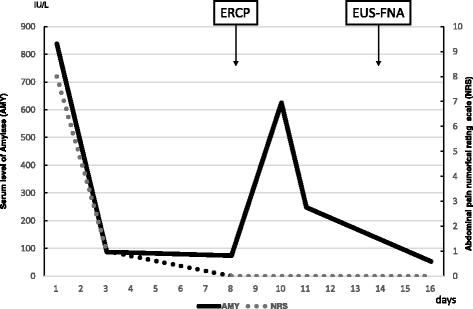
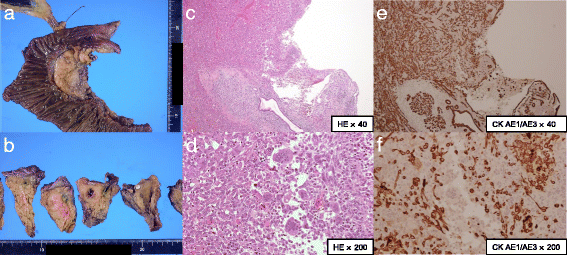
Case presentation: A 72-year-old Japanese woman presented with a diagnosis of acute pancreatitis, and a cystic lesion with slightly high density area was observed by computed tomography in her pancreatic head. In addition, endoscopic ultrasound revealed a heterogeneous lesion. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration showed pleomorphic atypical cells. We diagnosed anaplastic carcinoma of the pancreas. We resected the lesion, and she has shown no sign of recurrence for > 6 months. There are few reports of anaplastic carcinoma of the pancreas diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration and treated by surgery. Our analysis indicates that anaplastic carcinoma of the pancreas is more likely than typical ductal carcinomas to have cystic lesions with the tumor.
Conclusions: We report a case of anaplastic carcinoma of the pancreas diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration and subsequently resected with a clear margin. We speculate that anaplastic carcinoma of the pancreas is more likely to have cystic changes than pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. When we diagnose pancreas tumor as having cystic changes, anaplastic carcinoma of the pancreas should be considered one of the differential diagnoses.
Keywords: Anaplastic carcinoma of the pancreas; Cystic change; EUS-FNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The importance of endoscopic ultrasound fine-needle aspiration in the diagnosis of solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: two case reports.J Med Case Rep. 2018 Apr 26;12(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13256-018-1585-3. J Med Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29695287 Free PMC article.
-
Anaplastic (undifferentiated) carcinoma of pancreas, an uncommon variant: Diagnosed on endoscopic-guided fine needle aspiration.Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2023 Jul-Sep;66(3):648-651. doi: 10.4103/ijpm.ijpm_538_21. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37530362
-
Conventional versus contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration for diagnosis of solid pancreatic lesions: A prospective randomized trial.Pancreatology. 2015 Sep-Oct;15(5):538-541. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2015.06.005. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Pancreatology. 2015. PMID: 26145837 Clinical Trial.
-
Needle tract seeding recurrence of pancreatic cancer in the gastric wall with paragastric lymph node metastasis after endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration followed by pancreatectomy: a case report and literature review.BMC Gastroenterol. 2020 Jan 15;20(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-1159-x. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 31941458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Malignant pancreatic extra-gastrointestinal stromal tumor diagnosed by ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration cytology. A case report with a review of the literature.JOP. 2011 May 6;12(3):283-6. JOP. 2011. PMID: 21546710 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapidly Progressing Anaplastic Carcinoma of the Pancreas with Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma: An Autopsy Case Report.Intern Med. 2021 Jul 15;60(14):2235-2240. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.6181-20. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33612673 Free PMC article.
-
Early Recurrence of Pleomorphic-Type Anaplastic Pancreatic Carcinoma After Distal Pancreatectomy Causing Delayed-Onset Pancreatic Fistula: A Case Report.Cureus. 2025 May 18;17(5):e84316. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84316. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40385250 Free PMC article.
-
The Utility of Endoscopic-Ultrasonography-Guided Tissue Acquisition for Solid Pancreatic Lesions.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 19;12(3):753. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030753. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cephalic undifferentiated carcinoma with osteoclast-like giant cells arising from the main pancreatic duct: case report and literature review.Arch Clin Cases. 2021 Oct 27;6(1):6-21. doi: 10.22551/2019.22.0601.10148. eCollection 2019. Arch Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 34754903 Free PMC article.
-
Rare pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma variants and other malignant epithelial tumors: a comprehensive clinical and radiologic review.Jpn J Radiol. 2025 Aug;43(8):1239-1260. doi: 10.1007/s11604-025-01777-7. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Jpn J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40214914 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

