IP6 is an HIV pocket factor that prevents capsid collapse and promotes DNA synthesis
- PMID: 29848441
- PMCID: PMC6039178
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.35335
IP6 is an HIV pocket factor that prevents capsid collapse and promotes DNA synthesis
Abstract
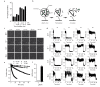
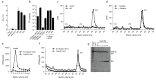
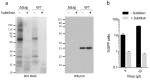
The HIV capsid is semipermeable and covered in electropositive pores that are essential for viral DNA synthesis and infection. Here, we show that these pores bind the abundant cellular polyanion IP6, transforming viral stability from minutes to hours and allowing newly synthesised DNA to accumulate inside the capsid. An arginine ring within the pore coordinates IP6, which strengthens capsid hexamers by almost 10°C. Single molecule measurements demonstrate that this renders native HIV capsids highly stable and protected from spontaneous collapse. Moreover, encapsidated reverse transcription assays reveal that, once stabilised by IP6, the accumulation of new viral DNA inside the capsid increases >100 fold. Remarkably, isotopic labelling of inositol in virus-producing cells reveals that HIV selectively packages over 300 IP6 molecules per infectious virion. We propose that HIV recruits IP6 to regulate capsid stability and uncoating, analogous to picornavirus pocket factors. HIV-1/IP6/capsid/co-factor/reverse transcription.
Keywords: HIV; IP6; capsid; human; infectious disease; microbiology; molecular biophysics; structural biology.
© 2018, Mallery et al.
Conflict of interest statement
DM, CM, WM, CD, DJ, MA, KB, GT, AS, TB, LJ No competing interests declared
Figures
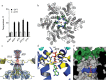
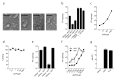
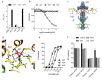
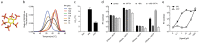
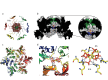
Comment in
-
The secrets of the stability of the HIV-1 capsid.Elife. 2018 Jul 31;7:e38895. doi: 10.7554/eLife.38895. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30063007 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambrose Z, Lee K, Ndjomou J, Xu H, Oztop I, Matous J, Takemura T, Unutmaz D, Engelman A, Hughes SH, KewalRamani VN. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 capsid mutation N74D alters cyclophilin A dependence and impairs macrophage infection. Journal of Virology. 2012;86:4708–4714. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05887-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G0801172/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G9721629/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_1201814/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12018/4/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U105181010/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00012/4/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 206248/Z/17/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_U122680443/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U105181010/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 339223/ERC_/European Research Council/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

