The Calcium-Sensing Receptor Increases Activity of the Renal NCC through the WNK4-SPAK Pathway
- PMID: 29848507
- PMCID: PMC6050918
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2017111155
The Calcium-Sensing Receptor Increases Activity of the Renal NCC through the WNK4-SPAK Pathway
Abstract
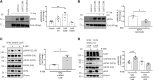
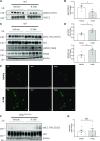
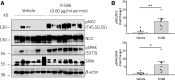
Background Hypercalciuria can result from activation of the basolateral calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR), which in the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop controls Ca2+ excretion and NaCl reabsorption in response to extracellular Ca2+ However, the function of CaSR in the regulation of NaCl reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is unknown. We hypothesized that CaSR in this location is involved in activating the thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter (NCC) to prevent NaCl loss.Methods We used a combination of in vitro and in vivo models to examine the effects of CaSR on NCC activity. Because the KLHL3-WNK4-SPAK pathway is involved in regulating NaCl reabsorption in the DCT, we assessed the involvement of this pathway as well.Results Thiazide-sensitive 22Na+ uptake assays in Xenopus laevis oocytes revealed that NCC activity increased in a WNK4-dependent manner upon activation of CaSR with Gd3+ In HEK293 cells, treatment with the calcimimetic R-568 stimulated SPAK phosphorylation only in the presence of WNK4. The WNK4 inhibitor WNK463 also prevented this effect. Furthermore, CaSR activation in HEK293 cells led to phosphorylation of KLHL3 and WNK4 and increased WNK4 abundance and activity. Finally, acute oral administration of R-568 in mice led to the phosphorylation of NCC.Conclusions Activation of CaSR can increase NCC activity via the WNK4-SPAK pathway. It is possible that activation of CaSR by Ca2+ in the apical membrane of the DCT increases NaCl reabsorption by NCC, with the consequent, well known decrease of Ca2+ reabsorption, further promoting hypercalciuria.
Keywords: Na transport; distal tubule; diuretics; hypertension.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Glucose/Fructose Delivery to the Distal Nephron Activates the Sodium-Chloride Cotransporter via the Calcium-Sensing Receptor.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023 Jan 1;34(1):55-72. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2021121544. Epub 2022 Oct 26. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36288902 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the WNK4-SPAK-NCC pathway by the calcium-sensing receptor.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2023 Sep 1;32(5):451-457. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000915. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2023. PMID: 37530086 Review.
-
Kidney-specific WNK1 isoform (KS-WNK1) is a potent activator of WNK4 and NCC.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Sep 1;315(3):F734-F745. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00145.2018. Epub 2018 May 30. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29846116 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of the WNK4-SPAK/OSR1 pathway has a minor effect on baseline NKCC2 phosphorylation.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 Jan 1;326(1):F39-F56. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00100.2023. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024. PMID: 37881876 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of Na+Cl- cotransporter by with-no-lysine kinase 4.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016 Sep;25(5):417-23. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000247. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 27322883 Review.
Cited by
-
Navigating the multifaceted intricacies of the Na+-Cl- cotransporter, a highly regulated key effector in the control of hydromineral homeostasis.Physiol Rev. 2024 Jul 1;104(3):1147-1204. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00027.2023. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Physiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38329422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood pressure effects of sodium transport along the distal nephron.Kidney Int. 2022 Dec;102(6):1247-1258. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.09.009. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Kidney Int. 2022. PMID: 36228680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How the kidney regulates magnesium: a modelling study.R Soc Open Sci. 2024 Mar 20;11(3):231484. doi: 10.1098/rsos.231484. eCollection 2024 Mar. R Soc Open Sci. 2024. PMID: 38511086 Free PMC article.
-
The serine-threonine protein phosphatases that regulate the thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter.Front Physiol. 2023 Feb 15;14:1100522. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1100522. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36875042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms for the modulation of blood pressure and potassium homeostasis by the distal convoluted tubule.EMBO Mol Med. 2022 Feb 7;14(2):e14273. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202114273. Epub 2021 Dec 20. EMBO Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34927382 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brown EM, Gamba G, Riccardi D, Lombardi M, Butters R, Kifor O, et al. : Cloning and characterization of an extracellular Ca(2+)-sensing receptor from bovine parathyroid. Nature 366: 575–580, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Riccardi D, Hall AE, Chattopadhyay N, Xu JZ, Brown EM, Hebert SC: Localization of the extracellular Ca2+/polyvalent cation-sensing protein in rat kidney. Am J Physiol 274: F611–F622, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Riccardi D, Lee WS, Lee K, Segre GV, Brown EM, Hebert SC: Localization of the extracellular Ca(2+)-sensing receptor and PTH/PTHrP receptor in rat kidney. Am J Physiol 271: F951–F956, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Riccardi D, Valenti G: Localization and function of the renal calcium-sensing receptor. Nat Rev Nephrol 12: 414–425, 2016 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

