Epidemiology and Clinical Features of Adult Patients with Psoriasis in Malaysia: 10-Year Review from the Malaysian Psoriasis Registry (2007-2016)
- PMID: 29849578
- PMCID: PMC5937568
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/4371471
Epidemiology and Clinical Features of Adult Patients with Psoriasis in Malaysia: 10-Year Review from the Malaysian Psoriasis Registry (2007-2016)
Abstract
Background: Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting 2-3% of the general population.
Aim: To evaluate the epidemiology and clinical characteristics of patients with psoriasis who seek treatment in outpatient dermatology clinics throughout hospitals in Malaysia.
Materials and methods: Data were obtained from the Malaysian Psoriasis Registry (MPR). All patients (aged 18 and above) who were notified to the registry from July 2017 to December 2017 were included in this study.
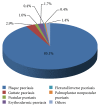
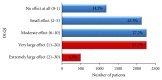
Results: Among 15,794 patients, Malays were the most common (50.4%), followed by Chinese (21.4%), Indian (17.6%), and others (10.6%). The mean age onset of psoriasis for our study population was 35.14 ± 16.16 years. Male to female ratio was 1.3 : 1. 23.1% of patients had positive family history of psoriasis. The most common clinical presentation was chronic plaque psoriasis (85.1%), followed by guttate psoriasis (2.9%), erythrodermic psoriasis (1.7%), and pustular psoriasis (1.0%). Majority of our patients (76.6%) had a mild disease with BSA < 10%. 57.1% of patients had nail involvement, while arthropathy was seen in 13.7% of patients. Common triggers of the disease include stress (48.3%), sunlight (24.9%), and infection (9.1%). Comorbidities observed include obesity (24.3%), hypertension (25.6%), hyperlipidemia (18%), diabetes mellitus (17.2%), ischaemic heart disease (5.4%), and cerebrovascular disease (1.6%). The mean DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) was 8.5 ± 6.6. One-third (33.1%) of the patients had a DLQI score of more than 10, while 14.2% of patients reported no effect at all.
Conclusion: Our study on the epidemiological data of adult patients with psoriasis in Malaysia showed a similar clinical profile and outcome when compared to international published studies on the epidemiology of psoriasis.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources