Pulmonary Thromboembolism Presenting with Recurrent Bradycardia and Hypotension
- PMID: 29849680
- PMCID: PMC5960231
Pulmonary Thromboembolism Presenting with Recurrent Bradycardia and Hypotension
Abstract
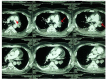
Recurrent short episodes of bradycardia and hypotension are rarely reported as clinical manifestations of pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE). We report a case of acute massive PTE presenting with dyspnea, burning chest pain with physical activity, and recurrent transient bradycardia and hypotension at rest. Echocardiography showed a left ventricular ejection fraction of 45% with global hypokinesia. Computed tomography angiography showed a large pulmonary thromboembolism. Lytic therapy improved the right ventricular function, and the pulmonary artery pressure decreased to 38 mmHg. Recurrent bradycardia and transient hypotension at rest with syncope on activity and recovery without treatment are not common and may suggest a vasovagal mechanism. Evaluation of patients with these clinical findings could enable early diagnosis and treatment of acute PTE, with decreased morbidity and mortality.
Keywords: Bradycardia; Pulmonary thromboembolism; Syncope.
Figures
References
-
- Torbicki A, Perrier A, Konstantinides S, Agnelli G, Galiè N, Pruszczyk P, et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2008;29(18):2276–315. - PubMed
-
- Cushman M, Tsai AW, White RH, Heckbert SR, Rosamond WD, Enright P, Folsom AR. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in two cohorts: the longitudinal investigation of thromboembolism etiology. Am J Med 2004;117(1):19–25. - PubMed
-
- Petrov DB. Appearance of right bundle branch block in electrocardiograms of patients with pulmonary embolism as a marker for obstruction of the main pulmonary trunk. J Electrocardiol 2001;34(3):185–8. - PubMed
-
- Alyan Ö, Özdemir Ö, Kaçmaz F, Topaloğlu S. Complete atrioventricular block and syncope during acute pulmonary thromboembolism. Archives of the Turkish Society of Cardiology 2007;35(7):433–5.
-
- Thorén P. Reflex bradycardia elicited from left ventricular receptors during acute severe hypoxia in cats. Acta Physiol Scand 1973;87(1):103–12. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources