Isopropyl Caffeate: A Caffeic Acid Derivative-Antioxidant Potential and Toxicity
- PMID: 29849905
- PMCID: PMC5932986
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/6179427
Isopropyl Caffeate: A Caffeic Acid Derivative-Antioxidant Potential and Toxicity
Abstract
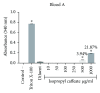
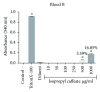
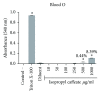
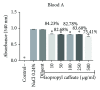
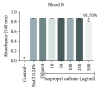
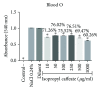
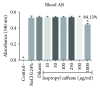
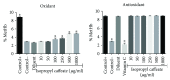
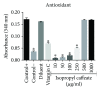
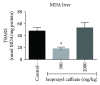
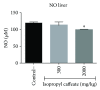
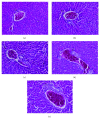
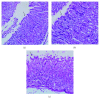
Phenolic compounds, among them isopropyl caffeate, possess antioxidant potential, but not without toxicity and/or adverse effects. The present study aimed to evaluate the antioxidant activity and toxicity of isopropyl caffeate through in silico, in vitro and in vivo testing. The results showed that isopropyl caffeate presents no significant theoretical risk of toxicity, with likely moderate bioactivity: GPCR binding, ion channel modulation, nuclear receptor binding, and enzyme inhibition. Isopropyl caffeate induced hemolysis only at the concentrations of 500 and 1000 μg/ml. We observed types A and O erythrocyte protection from osmotic stress, no oxidation of erythrocytes, and even sequestrator and antioxidant behavior. However, moderate toxicity, according to the classification of GHS, was demonstrated through depressant effects on the central nervous system, though there was no influence on water and food consumption or on weight gain, and it did present possible hepatoprotection. We conclude that the effects induced by isopropyl caffeate are due to its antioxidant activity, capable of preventing production of free radicals and oxidative stress, a promising molecule with pharmacological potential.
Figures


References
-
- Damasceno S. S., Dantas B. B., Ribeiro-Filho J., Antônio M Araújo D., Galberto M da Costa J. Chemical properties of caffeic and ferulic acids in biological system: implications in cancer therapy. A review. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2017;23(20):3015–3023. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666161208145508. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang H., Tsao R. Dietary polyphenols, oxidative stress and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Current Opinion in Food Science. 2016;8:33–42. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2016.02.002. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

