Stem cells as delivery vehicles for regenerative medicine-challenges and perspectives
- PMID: 29849930
- PMCID: PMC5973910
- DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v10.i5.43
Stem cells as delivery vehicles for regenerative medicine-challenges and perspectives
Abstract
The use of stem cells as carriers for therapeutic agents is an appealing modality for targeting tissues or organs of interest. Combined delivery of cells together with various information molecules as therapeutic agents has the potential to enhance, modulate or even initiate local or systemic repair processes, increasing stem cell efficiency for regenerative medicine applications. Stem-cell-mediated delivery of genes, proteins or small molecules takes advantage of the innate capability of stem cells to migrate and home to injury sites. As the native migratory properties are affected by in vitro expansion, the existent methods for enhancing stem cell targeting capabilities (modified culture methods, genetic modification, cell surface engineering) are described. The role of various nanoparticles in equipping stem cells with therapeutic small molecules is revised together with their class-specific advantages and shortcomings. Modalities to circumvent common challenges when designing a stem-cell-mediated targeted delivery system are described as well as future prospects in using this approach for regenerative medicine applications.
Keywords: Delivery agents; Nanoparticles; Regenerative medicine; Stem cells; Targeted delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures
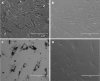
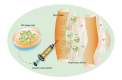
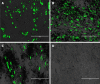
References
-
- Mimeault M, Hauke R, Batra SK. Stem cells: a revolution in therapeutics-recent advances in stem cell biology and their therapeutic applications in regenerative medicine and cancer therapies. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;82:252–264. - PubMed
-
- Badowski MS, Zhang T, Tsang TC, Harris DT. Chimeric antigen receptors for stem cell based immunotherapy. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2009;8:53–63. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz SD, Regillo CD, Lam BL, Eliott D, Rosenfeld PJ, Gregori NZ, Hubschman JP, Davis JL, Heilwell G, Spirn M, et al. Human embryonic stem cell-derived retinal pigment epithelium in patients with age-related macular degeneration and Stargardt's macular dystrophy: follow-up of two open-label phase 1/2 studies. Lancet. 2015;385:509–516. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

