Apelin-13 Is an Early Promoter of Cytoskeleton and Tight Junction in Diabetic Macular Edema via PI-3K/Akt and MAPK/Erk Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 29850504
- PMCID: PMC5904819
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/3242574
Apelin-13 Is an Early Promoter of Cytoskeleton and Tight Junction in Diabetic Macular Edema via PI-3K/Akt and MAPK/Erk Signaling Pathways
Abstract
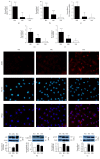
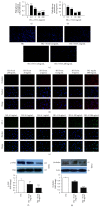
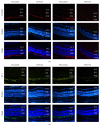
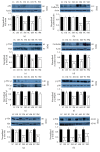
Diabetic macular edema is major cause of vision loss associated with diabetic retinopathy. Breakdown of blood-retinal barrier, especially inner BRB, is an early event in pathogenesis of DR. Apelin, an endogenous ligand of APJ, mediates angiogenesis and is involved in the development of DR. The present study aimed to investigate effects and mechanism of apelin-13 in vascular permeability during DME. We verified apelin-13 was upregulated in DME patients' vitreous. High glucose incubation led to a progressive increase of apelin-13, APJ, cytoskeleton, and tight junction proteins, including VE-Cadherin, FAK, Src, ZO-1, and occludin. Apelin-13 promoted HRMEC proliferation and migration and phosphorylation of both cytoskeleton and tight junction under both normal and high glucose conditions. Besides, apelin-13 activated PI-3K/Akt and MAPK/Erk signaling pathways, including PLCγ1, p38, Akt, and Erk both in HRMEC and in C57BL/6 mice. Meanwhile, F13A performed opposite effects compared with apelin-13. In in vivo study, apelin-13 was also upregulated in retina of db/db mice. Taken together, apelin-13 increased biologic activity of HRMEC, as well as expression of both cytoskeleton and tight junction in DME via PI-3K/Akt and MAPK/Erk signaling pathways. Apelin-13 as an early promoter of vascular permeability may offer a new perspective strategy in early treatment of DR.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Apelin induces the proliferation, migration and expression of cytoskeleton and tight junction proteins in human RPE cells via PI-3K/Akt and MAPK/Erk signaling pathways.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Nov 1;10(11):10711-10729. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966415 Free PMC article.
-
Apelin-13 induces proliferation, migration, and collagen I mRNA expression in human RPE cells via PI3K/Akt and MEK/Erk signaling pathways.Mol Vis. 2013 Nov 7;19:2227-36. eCollection 2013. Mol Vis. 2013. PMID: 24227918 Free PMC article.
-
Apelin-13 Protects against Ischemic Blood-Brain Barrier Damage through the Effects of Aquaporin-4.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;44(1-2):10-25. doi: 10.1159/000460261. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017. PMID: 28402976
-
Multiple roles of apelin/APJ system in eye diseases.Peptides. 2022 Jun;152:170767. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2022.170767. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Peptides. 2022. PMID: 35181348 Review.
-
Regulation of blood-retinal barrier cell-junctions in diabetic retinopathy.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Nov;161:105115. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105115. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32750417 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-503/Apelin-12 mediates high glucose-induced microvascular endothelial cells injury via JNK and p38MAPK signaling pathway.Regen Ther. 2020 Jan 17;14:111-118. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2019.12.002. eCollection 2020 Jun. Regen Ther. 2020. PMID: 31989001 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Apelin/APJ in a Mouse Model of Oxygen-induced Retinopathy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Jul 1;61(8):47. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.8.47. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32729912 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key lipid metabolites during metabolic dysregulation in the diabetic retinopathy disease mouse model and efficacy of Keluoxin capsule using an UHPLC-MS-based non-targeted lipidomics approach.RSC Adv. 2021 Feb 1;11(10):5491-5505. doi: 10.1039/d0ra00343c. eCollection 2021 Jan 28. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35423075 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insights into the alterations and regulation of the AKT signaling pathway in diabetic retinopathy.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Nov 17;9(1):418. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01717-2. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37978169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the therapeutic potential: Apelin-13's neuroprotective effects foster sustained functional motor recovery in a rat model of Huntington's disease.Anat Cell Biol. 2024 Sep 30;57(3):419-430. doi: 10.5115/acb.23.284. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Anat Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39079710 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

