Effect of Repeated Injection of Iodixanol on Renal Function in Healthy Wistar Rats Using Functional MRI
- PMID: 29850557
- PMCID: PMC5904815
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/7272485
Effect of Repeated Injection of Iodixanol on Renal Function in Healthy Wistar Rats Using Functional MRI
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the optimal time interval of repeated intravenous injections of iodixanol in rat model and to identify the injury location and causes of renal damage in vivo.
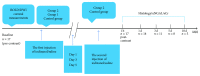
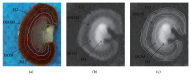
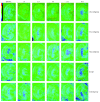
Materials and methods: Rats were randomly divided into Control group, Group 1 with one iodixanol injection, and Group 2 with two iodixanol injections. Group 2 was subdivided into 3 cohorts according to the interval between the first and second iodixanol injections as 1, 3, and 5 days, respectively. Blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) imaging and diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) were performed at 1 hour, 1 day, 3 days, 5 days, and 10 days after the application of solutions.
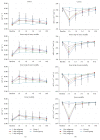
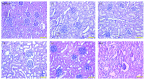
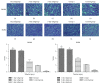
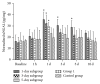
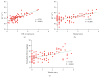
Results: Compared with Group 1 (7.2%), Group 2 produced a remarkable R2⁎ increment at the inner stripe of the renal outer medulla by 15.37% (P = 0.012), 14.83% (P = 0.046), and 13.53% (P > 0.05), respectively, at 1 hour after repeated injection of iodixanol. The severity of BOLD MRI to detect renal hypoxia was consistent with the expression of HIF-1α and R2⁎ was well correlated with HIF-1α expression (r = 0.704). The acute tubular injury was associated with urinary NGAL and increased significantly at 1 day.
Conclusions: Repetitive injection of iodixanol within a short time window can induce acute kidney injury, the impact of which on renal damage in rats disappears gradually 3-5 days after the injections.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficacy of preventive interventions for iodinated contrast-induced acute kidney injury evaluated by intrarenal oxygenation as an early marker.Invest Radiol. 2014 Oct;49(10):647-52. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000065. Invest Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24872003 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of intrarenal oxygenation in iodinated contrast-induced acute kidney injury-susceptible rats by blood oxygen level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging.Invest Radiol. 2014 Jun;49(6):403-10. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000031. Invest Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24566288 Free PMC article.
-
Application of BOLD MRI and DTI for the evaluation of renal effect related to viscosity of iodinated contrast agent in a rat model.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017 Nov;46(5):1320-1331. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25683. Epub 2017 Mar 1. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017. PMID: 28248433
-
Effect of iodinated contrast medium in diabetic rat kidneys as evaluated by blood-oxygenation-level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging and urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin.Invest Radiol. 2015 Jun;50(6):392-6. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000141. Invest Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25668748 Free PMC article.
-
Significant perturbation in renal functional magnetic resonance imaging parameters and contrast retention for iodixanol compared with iopromide: an experimental study using blood-oxygen-level-dependent/diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography in rats.Invest Radiol. 2014 Nov;49(11):699-706. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000073. Invest Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24879299
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Renal Pathophysiological Processes Induced by an Iodinated Contrast Agent in a Diabetic Rabbit Model Using Intravoxel Incoherent Motion and Blood Oxygenation Level-Dependent Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Korean J Radiol. 2019 May;20(5):830-843. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.0757. Korean J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30993934 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

