Basement Membranes in Development and Disease
- PMID: 29853176
- PMCID: PMC6701859
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2018.02.005
Basement Membranes in Development and Disease
Abstract
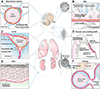
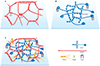
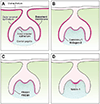
The basement membrane is a thin but dense, sheet-like specialized type of extracellular matrix that has remarkably diverse functions tailored to individual tissues and organs. Tightly controlled spatial and temporal changes in its composition and structure contribute to the diversity of basement membrane functions. These different basement membranes undergo dynamic transformations throughout animal life, most notably during development. Numerous developmental mechanisms are regulated or mediated by basement membranes, often by a combination of molecular and mechanical processes. A particularly important process involves cell transmigration through a basement membrane because of its link to cell invasion in disease. While developmental and disease processes share some similarities, what clearly distinguishes the two is dysregulation of cells and extracellular matrices in disease. With its relevance to many developmental and disease processes, the basement membrane is a vitally important area of research that may provide novel insights into biological mechanisms and development of innovative therapeutic approaches. Here we present a review of developmental and disease dynamics of basement membranes in Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila, and vertebrates.
Keywords: Basement membrane; Basement membrane pores; Cancer; Cell migration; Development; Extracellular matrix; Invasion; Morphogenesis; Proliferation.
2018 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Aumailley M, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Carter WG, Deutzmann R, Edgar D, Ekblom P, Engel J, Engvall E, Hohenester E, Jones JC, Kleinman HK, Marinkovich MP, Martin GR, Mayer U, Meneguzzi G, Miner JH, Miyazaki K, Patarroyo M, Paulsson M, Quaranta V, Sanes JR, Sasaki T, Sekiguchi K, Sorokin LM, Talts JF, Tryggvason K, Uitto J, Virtanen I, von der Mark K, Wewer UM, Yamada Y, Yurchenco PD, 2005. A simplified laminin nomenclature. Matrix Biol 24, 326–332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

