Cartilage and bone damage in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 29853727
- PMCID: PMC5974634
- DOI: 10.5114/reum.2018.75523
Cartilage and bone damage in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
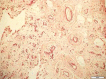
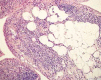
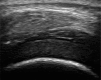
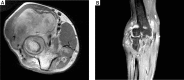
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), which is a chronic inflammatory disease with a multifactorial aetiology, leads to partial or permanent disability in the majority of patients. It is characterised by persistent synovitis and formation of pannus, i.e. invasive synovial tissue, which ultimately leads to destruction of the cartilage, subchondral bone, and soft tissues of the affected joint. Moreover, inflammatory infiltrates in the subchondral bone, which can lead to inflammatory cysts and later erosions, play an important role in the pathogenesis of RA. These inflammatory infiltrates can be seen in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as bone marrow oedema (BME). BME is observed in 68-75% of patients in early stages of RA and is considered a precursor of rapid disease progression. The clinical significance of synovitis and bone marrow oedema as precursors of erosions is well established in daily practice, and synovitis, BME, cysts, hyaline cartilage defects and bone erosions can be detected by ultrasonography (US) and MRI. A less explored subject is the inflammatory and destructive potential of intra- and extra-articular fat tissue, which can also be evaluated in US and MRI. Finally, according to certain hypotheses, hyaline cartilage damage may trigger synovitis and lead to irreversible joint damage, and MRI may be used for preclinical detection of cartilage biochemical abnormalities. This review discusses the pathomechanisms that lead to articular cartilage and bone damage in RA, including erosion precursors such as synovitis and osteitis and panniculitis, as well as the role of imaging techniques employed to detect early cartilage damage and bone erosions.
Keywords: cartilage; erosions; magnetic resonance imaging; rheumatoid arthritis; synovitis; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Buchbender C, Ostendorf B, Mattes-György K, et al. Synovitis and bone inflammation in early rheumatoid arthritis: high-resolution multi-pinhole SPECT versus MRI. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2013;19:20–24. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Steiner G. Does damage cause inflammation? Revisiting the link between joint damage and inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:159–162. - PubMed
-
- Miese FR, Ostendorf B, Wittsack H-J, et al. Metacarpophalangeal Joints in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Delayed Gadolinium-enhanced MR Imaging of Cartilage – A Feasibility Study. Radiology. 2010;257:441–447. - PubMed
-
- Narváez JA, Narváez J, De Lama E, et al. MR imaging of early rheumatoid arthritis. Radiographics. 2010;30:143–163. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
