Craniocervical Dissections: Radiologic Findings, Pitfalls, Mimicking Diseases: A Pictorial Review
- PMID: 29853818
- PMCID: PMC5902863
- DOI: 10.2174/1573405613666170403102235
Craniocervical Dissections: Radiologic Findings, Pitfalls, Mimicking Diseases: A Pictorial Review
Abstract
Background: Craniocervical Dissections (CCD) are a crucial emergency state causing 20% of strokes in patients under the age of 45. Although DSA (digital substraction angiography) is regarded as the gold standard, noninvasive methods of CT, CTA and MRI, MRA are widely used for diagnosis.
Aim: Our aim is to illustrate noninvasive imaging findings in CCD.
Conclusion: Emphasizing on diagnostic pitfalls, limitations and mimicking diseases.
Keywords: CT; CTA; Craniocervical dissection; DSA; MRA; MRI.
Figures
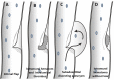
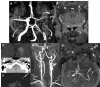
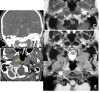
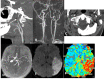
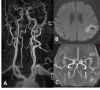
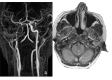
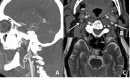



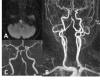
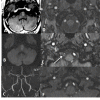
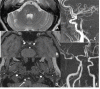
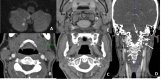
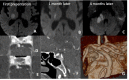
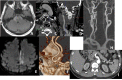





References
-
- Nagumo K. N akamori A, Kojima S. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2003;43:313–321. [Spontaneous intracranial internal carotid artery dissection: 6 case reports and a review of 39 cases in the literature]. - PubMed
-
- Volker W., Besselmann M., Dittrich R., et al. Generalized arteriopathy in patients with cervical artery dissection. Neurology. 2005;64:1508–1513. - PubMed
-
- Fusca M.R., Harrigan M.R. Cerebrovascular dissections--a review part I: Spontaneous dissections. Neurosurgery. 2011;68:242–257. - PubMed
-
- Benninger D.H., Gandjour J., Georgiadis D., et al. Benign long-term outcome of conservatively treated cervical aneurysms due to carotid dissection. Neurology. 2007;69:486–487. - PubMed
-
- Caso V., Paciaroni M., Corea F., et al. Recanalization of cervical artery dissection: influencing factors and role in neurological outcome. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2004;17:93–97. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
