Predicting Inpatient Acute Kidney Injury over Different Time Horizons: How Early and Accurate?
- PMID: 29854121
- PMCID: PMC5977670
Predicting Inpatient Acute Kidney Injury over Different Time Horizons: How Early and Accurate?
Abstract
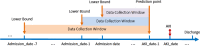
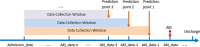
Incidence of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) has increased dramatically over the past two decades due to rising prevalence of comorbidities and broadening repertoire of nephrotoxic medications. Hospitalized patients with AKI are at higher risk for complications and mortality, thus early recognition of AKI is crucial. Building AKI prediction models based on electronic medical records (EMRs) can enable early recognition of high-risk patients, facilitate prevention of iatrogenically induced AKI events, and improve patient outcomes. This study builds machine learning models to predict hospital-acquired AKI over different time horizons using EMR data. The study objectives are to assess (1) whether early AKI prediction is possible; (2) whether information prior to admission improves prediction; (3) what type of risk factors affect AKI prediction the most. Evaluation results showed a good cross-validated AUC of 0.765 for predicting AKI events 1-day prior and adding data prior to admission did not improve model performance.
Figures
References
-
- Fortescue EB, Bates DW, Chertow GM. Predicting acute renal failure after coronary bypass surgery: crossvalidation of two risk-stratification algorithms. Kidney international. 2000 Jun;57(6):2594–602. - PubMed
-
- Hou SH, Bushinsky DA, Wish JB, Cohen JJ, Harrington JT. Hospital-acquired renal insufficiency: a prospective study. The American journal of medicine. 1983 Feb;74(2):243–8. - PubMed
-
- Wijeysundera DN, Karkouti K, Dupuis JY, et al. Derivation and validation of a simplified predictive index for renal replacement therapy after cardiac surgery. JAMA. 2007 Apr 25;297(16):1801–9. - PubMed
-
- Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, Bonventre JV, Bates DW. Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and costs in hospitalized patients. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: JASN. 2005 Nov;16(11):3365–70. - PubMed
-
- Liano F, Junco E, Pascual J, Madero R, Verde E. The spectrum of acute renal failure in the intensive care unit compared with that seen in other settings. The Madrid Acute Renal Failure Study Group. Kidney international Supplement. 1998 May;66:S16–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous