Forecasting obesity prevalence in Korean adults for the years 2020 and 2030 by the analysis of contributing factors
- PMID: 29854331
- PMCID: PMC5974071
- DOI: 10.4162/nrp.2018.12.3.251
Forecasting obesity prevalence in Korean adults for the years 2020 and 2030 by the analysis of contributing factors
Abstract
Background/objectives: There are few studies that forecast the future prevalence of obesity based on the predicted prevalence model including contributing factors. The present study aimed to identify factors associated with obesity and construct forecasting models including significant contributing factors to estimate the 2020 and 2030 prevalence of obesity and abdominal obesity.
Subjects/methods: Panel data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and national statistics from the Korean Statistical Information Service were used for the analysis. The study subjects were 17,685 male and 24,899 female adults aged 19 years or older. The outcome variables were the prevalence of obesity (body mass index ≥ 25 kg/m2) and abdominal obesity (waist circumference ≥ 90 cm for men and ≥ 85 cm for women). Stepwise logistic regression analysis was used to select significant variables from potential exposures.
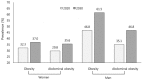
Results: The survey year, age, marital status, job status, income status, smoking, alcohol consumption, sleep duration, psychological factors, dietary intake, and fertility rate were found to contribute to the prevalence of obesity and abdominal obesity. Based on the forecasting models including these variables, the 2020 and 2030 estimates for obesity prevalence were 47% and 62% for men and 32% and 37% for women, respectively.
Conclusions: The present study suggested an increased prevalence of obesity and abdominal obesity in 2020 and 2030. Lifestyle factors were found to be significantly associated with the increasing trend in obesity prevalence and, therefore, they may require modification to prevent the rising trend.
Keywords: Obesity; abdominal fat; forecasting; prevalence; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The author declares no potential conflicts of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2015: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VI-3) Cheongju: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2016.
-
- Lee SM, Yoon Y, Baek J, Hyun K, Gang H. Socio-economic Impacts of Major Health Risk Factors and Evaluation on Effects of Regulatory Policy. Seoul: Health Insurance Policy Institute of National Health Insurance Service; 2015.
-
- Reidpath DD, Burns C, Garrard J, Mahoney M, Townsend M. An ecological study of the relationship between social and environmental determinants of obesity. Health Place. 2002;8:141–145. - PubMed
-
- Finkelstein EA, Khavjou OA, Thompson H, Trogdon JG, Pan L, Sherry B, Dietz W. Obesity and severe obesity forecasts through 2030. Am J Prev Med. 2012;42:563–570. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources