Delayed-start analysis: Mild Alzheimer's disease patients in solanezumab trials, 3.5 years
- PMID: 29854931
- PMCID: PMC5975050
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trci.2015.06.006
Delayed-start analysis: Mild Alzheimer's disease patients in solanezumab trials, 3.5 years
Abstract
Introduction: Solanezumab is an anti-amyloid monoclonal antibody in clinical testing for treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Its mechanism suggests the possibility of slowing the progression of AD.
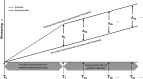
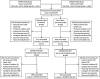
Methods: A possible disease-modifying effect of solanezumab was assessed using a new statistical method including noninferiority testing. Performance differences were compared during the placebo-controlled period with performance differences after the placebo patients crossed over to solanezumab in the delayed-start period.
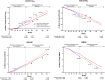
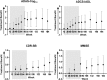
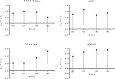
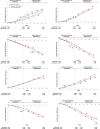
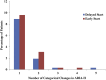
Results: Noninferiority of the 14-item Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive subscale (ADAS-Cog14) and Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study Activities of Daily Living inventory instrumental items (ADCS-iADL) differences was met through 132 weeks, indicating that treatment differences observed in the placebo-controlled period remained, within a predefined margin, after the placebo group initiated solanezumab. Solanezumab was well tolerated, and no new safety concerns were identified.
Discussion: The results of this secondary analysis show that the mild subgroup of solanezumab-treated patients who initiated treatment early, at the start of the placebo-controlled period, retained an advantage at most time points in the delayed-start period.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Anti-amyloid-β antibody; Clinical trials; Delayed-start; Solanezumab.
Figures

References
-
- Leber P. Slowing the progression of Alzheimer disease: Methodologicalissues. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1997;11:S10–S21. - PubMed
-
- Olanow C.W., Rascol O., Hauser R., Feigin P.D., Jankovic J., Lang A. A double-blind, delayed-start trial of rasagiline in Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1268–1278. - PubMed
-
- Doody R.S., Geldmacher D.S., Gordon B., Perdomo C.A., Pratt R.D., Donepezil Study Group Open-label, multicenter, phase 3 extension study of the safety and efficacy of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2001;58:427–433. - PubMed
-
- Winblad B., Wimo A., Engedal K., Soininen H., Verhey F., Waldemar G. 3-year study of donepezil therapy in Alzheimer's disease: Effects of early and continuous therapy. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2006;21:353–363. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
