Combined treatment with memantine and galantamine-CR compared with galantamine-CR only in antidementia drug naïve patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 29854939
- PMCID: PMC5975055
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trci.2015.10.001
Combined treatment with memantine and galantamine-CR compared with galantamine-CR only in antidementia drug naïve patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Introduction: Several studies have tested the N-methyl-D-aspartate-receptor antagonist memantine as an add-on to pre-existing treatment with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. The objective of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of a combined memantine and galantamine-CR de novo regimen compared with galantamine-CR only treatment in never treated patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease (AD).
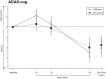
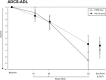
Methods: Antidementia drug-naïve participants (n = 232) with probable, mild-to-moderate AD, and mini-mental state examination scores between 15 and 26 (inclusive) were randomized to receive either 20 mg/day memantine plus 24 mg/day galantamine-CR or 24 mg/day galantamine-CR plus placebo in a 52-week, prospective, double-blind, controlled trial. The primary outcome measurement was the change on the Alzheimer's disease assessment scale-cognition score. Secondary measures comprised the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study-activities of daily living inventory and the clinical dementia rating.
Results: At the end of the trial, there were no statistically significant differences between the galantamine-CR/memantine combination and galantamine-CR only group in primary and secondary outcome measurements. The incidence and the severity of adverse events were similar between the groups.
Discussion: In this trial, memantine in combination with galantamine-CR did not show an advantage with respect to cognition, function, and behavior in previously never treated patients with mild-to-moderate AD. There were no significant differences in tolerability and safety between the groups. Thus, a de novo combination treatment results in no significant improvement in disease progression (current controlled trials number: NCT01921972).
Keywords: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor; Alzheimer's disease; Combination treatment; Dementia; Galantamine-CR; Memantine.
Figures


References
-
- Patel L., Grossberg G.T. Combination therapy for Alzheimer's disease. Drugs Aging. 2011;28:539–546. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt R., Hofer E., Bouwman F.H., Buerger K., Cordonnier C., Fladby T. EFNS-ENS/EAN Guideline on concomitant use of cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Neurol. 2015;22:889–898. - PubMed
-
- Tariot P.N., Farlow M.R., Grossberg G.T., Graham S.M., McDonald S., Gergel I. Memantine treatment in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer disease already receiving donepezil: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2004;291:317–324. - PubMed
-
- Grossberg G.T., Manes F., Allegri R.F., Gutierrez-Robledo L.M., Gloger S., Xie L. The safety, tolerability, and efficacy of once-daily memantine (28 mg): A multinational, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients with moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease taking cholinesterase inhibitors. CNS Drugs. 2013;27:469–478. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Porsteinsson A.P., Grossberg G.T., Mintzer J., Olin J.T., Memantine MEM-MD-12 Study Group Memantine treatment in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease already receiving a cholinesterase inhibitor: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2008;5:83–89. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
