General health status in Iranian diabetic patients assessed by short-form-36 questionnaire: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29855368
- PMCID: PMC5984362
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-018-0262-2
General health status in Iranian diabetic patients assessed by short-form-36 questionnaire: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus is one of the most prevalent diseases worldwide. Diabetes is a chronic disease associated with micro- and macro-vascular complications and deterioration in general health status. Therefore, the aim of this study was to estimate general health status among Iranian diabetic patients through a systematic review and meta-analysis of study utilizing the Short-Form-36 questionnaire.
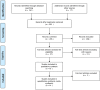
Methods: Searching the EMBASE, PubMed, ISI/Web of Sciences (WOS), MEDLINE via Ovid, PsycoINFO, as well as Iranian databases (MagIran, Iranmedex, and SID) from January 2000 to December 2017. The methodological quality of the studies was evaluated using the "A Cochrane Risk of Bias Assessment Tool: for Non-Randomized Studies of Interventions" (ACROBAT-NRSI). Random-effect model was used and the means were reported with their 95% confidence interval (CI). To evaluate the heterogeneity between studies, I2 test was used. Egger's regression test was used to assess the publication bias.
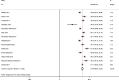
Results: Fourteen studies were retained in the final analysis. The mean general health status using SF-36 in diabetic patients of Iran was 51.9 (95% CI: 48.64 to 53.54). The mean physical component summary was 52.92 [95% CI: 49.46-56.38], while the mean mental component summary was 51.02 [95% CI: 46.87-55.16].
Conclusion: The findings of this study showed that general health status in Iranian diabetic patients is low. Health policymakers should work to improve the health status in these patients and take appropriate interventions.
Keywords: Diabetes; General health status; Iran; Meta-analysis; Short-Form-36 questionnaire.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Effects of a gluten-reduced or gluten-free diet for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 24;2(2):CD013556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35199850 Free PMC article.
-
Control interventions in randomised trials among people with mental health disorders.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 4;4(4):MR000050. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000050.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35377466 Free PMC article.
-
Final-impression techniques and materials for making complete and removable partial dentures.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 4;4(4):CD012256. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012256.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29617037 Free PMC article.
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for promoting habitual exercise in people living with and beyond cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Sep 19;9(9):CD010192. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010192.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30229557 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Challenges to Lifestyle Medicine for Type 2 Diabetes in Iran: A Synoptic Review.Am J Lifestyle Med. 2023 Apr 3;19(4):534-547. doi: 10.1177/15598276231167787. eCollection 2025 May-Jun. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2023. PMID: 40248659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychometric properties of the Persian Health Care Climate Questionnaire (HCCQ-P): assessment of type 2 diabetes care supportiveness in Iran.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2019 May 15;13:783-793. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S201400. eCollection 2019. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2019. PMID: 31190760 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review on quality of life (QoL) of patients with peritoneal metastasis (PM) who underwent pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC).Pleura Peritoneum. 2022 Apr 21;7(2):39-49. doi: 10.1515/pp-2021-0154. eCollection 2022 Jun 1. Pleura Peritoneum. 2022. PMID: 35812010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes of Endothelin-1 and Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Concentrations in Patients with Cervical Radiculopathy after Wrist-Ankle Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Hot Compression with Chinese Herbal Medicine.Genet Res (Camb). 2021 Dec 18;2021:5433742. doi: 10.1155/2021/5433742. eCollection 2021. Genet Res (Camb). 2021. PMID: 35002538 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

