Nanoparticles for Signaling in Biodiagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases
- PMID: 29857492
- PMCID: PMC6032068
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19061627
Nanoparticles for Signaling in Biodiagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases
Abstract
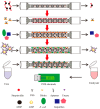
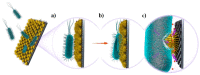
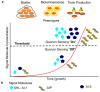
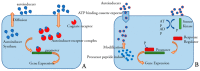
Advances in nanoparticle-based systems constitute a promising research area with important implications for the treatment of bacterial infections, especially against multidrug resistant strains and bacterial biofilms. Nanosystems may be useful for the diagnosis and treatment of viral and fungal infections. Commercial diagnostic tests based on nanosystems are currently available. Different methodologies based on nanoparticles (NPs) have been developed to detect specific agents or to distinguish between Gram-positive and Gram-negative microorganisms. Also, biosensors based on nanoparticles have been applied in viral detection to improve available analytical techniques. Several point-of-care (POC) assays have been proposed that can offer results faster, easier and at lower cost than conventional techniques and can even be used in remote regions for viral diagnosis. Nanoparticles functionalized with specific molecules may modulate pharmacokinetic targeting recognition and increase anti-infective efficacy. Quorum sensing is a stimuli-response chemical communication process correlated with population density that bacteria use to regulate biofilm formation. Disabling it is an emerging approach for combating its pathogenicity. Natural or synthetic inhibitors may act as antibiofilm agents and be useful for treating multi-drug resistant bacteria. Nanostructured materials that interfere with signal molecules involved in biofilm growth have been developed for the control of infections associated with biofilm-associated infections.
Keywords: bacterial infections; nanoparticles; point-of-care testing; quorum sensing; signaling; viral infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quorum quenching: role of nanoparticles as signal jammers in Gram-negative bacteria.Future Microbiol. 2019 Jan;14:61-72. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2018-0257. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Future Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30539663 Review.
-
Novel Nanotherapeutics as Next-generation Anti-infective Agents: Current Trends and Future Prospectives.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2020;17(4):457-468. doi: 10.2174/1570163816666190715120708. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2020. PMID: 31309893 Review.
-
Bactericidal, quorum quenching and anti-biofilm nanofactories: a new niche for nanotechnologists.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2017 Jun;37(4):525-540. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2016.1199010. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27684212 Review.
-
Biofilm formation mechanisms and targets for developing antibiofilm agents.Future Med Chem. 2015;7(4):493-512. doi: 10.4155/fmc.15.6. Future Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25875875 Review.
-
Antibiofilm agents: A new perspective for antimicrobial strategy.J Microbiol. 2017 Oct;55(10):753-766. doi: 10.1007/s12275-017-7274-x. Epub 2017 Sep 28. J Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28956348 Review.
Cited by
-
Grand Challenge in Human/Animal Virology: Unseen, Smallest Replicative Entities Shape the Whole Globe.Front Microbiol. 2020 Mar 18;11:431. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00431. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32256480 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Slow-sustained delivery of naloxone reduces typical naloxone-induced precipitated opioid withdrawal effects in male morphine-dependent mice.J Neurosci Res. 2022 Jan;100(1):339-352. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24627. Epub 2020 Aug 8. J Neurosci Res. 2022. PMID: 32772457 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Iron Nanoparticle-Based Materials in the Food Industry.Materials (Basel). 2023 Jan 12;16(2):780. doi: 10.3390/ma16020780. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36676517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bare Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Surface Tunability for Biomedical, Sensing and Environmental Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019 Nov 12;9(11):1608. doi: 10.3390/nano9111608. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31726776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olax scandens Mediated Biogenic Synthesis of Ag-Cu Nanocomposites: Potential Against Inhibition of Drug-Resistant Microbes.Front Chem. 2020 Feb 28;8:103. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00103. eCollection 2020. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 32185160 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

