Microtubules and Microtubule-Associated Proteins
- PMID: 29858272
- PMCID: PMC5983186
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022608
Microtubules and Microtubule-Associated Proteins
Abstract
Microtubules act as "railways" for motor-driven intracellular transport, interact with accessory proteins to assemble into larger structures such as the mitotic spindle, and provide an organizational framework to the rest of the cell. Key to these functions is the fact that microtubules are "dynamic." As with actin, the polymer dynamics are driven by nucleotide hydrolysis and influenced by a host of specialized regulatory proteins, including microtubule-associated proteins. However, microtubule turnover involves a surprising behavior-termed dynamic instability-in which individual polymers switch stochastically between growth and depolymerization. Dynamic instability allows microtubules to explore intracellular space and remodel in response to intracellular and extracellular cues. Here, we review how such instability is central to the assembly of many microtubule-based structures and to the robust functioning of the microtubule cytoskeleton.
Copyright © 2018 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
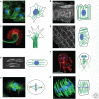

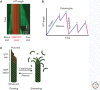
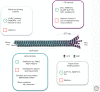
References
-
- Ada R, Kilmartin JV. 2000. Spindle pole body duplication: A model for centrosome duplication? Trends Cell Biol 10: 329–335. - PubMed
-
- Akhmanova A, Hoogenraad CC. 2015. Microtubule minus-end-targeting proteins. Curr Biol 25: R162–R171. - PubMed
-
- Akhmanova A, Steinmetz MO. 2008. Tracking the ends: A dynamic protein network controls the fate of microtubule tips. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9: 309–322. - PubMed
-
- Akhmanova A, Steinmetz MO. 2015. Control of microtubule organization and dynamics: Two ends in the limelight. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16: 711–726. - PubMed
-
- Akhmanova A, Stehbens SJ, Yap AS. 2009. Touch, grasp, deliver and control: Functional cross-talk between microtubules and cell adhesions. Traffic 10: 268–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
