Trends in Prevalence and Control of Hypertension According to the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) Guideline
- PMID: 29858369
- PMCID: PMC6015372
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.118.008888
Trends in Prevalence and Control of Hypertension According to the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) Guideline
Abstract
Background: Hypertension is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality. Compared with prior guidelines, the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) hypertension guideline recommends lower blood pressure thresholds for defining hypertension, for initiating antihypertensive medication, and for antihypertensive medication treatment goals.
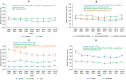
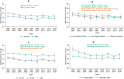
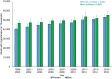
Methods and results: To better understand potential impacts of the 2017 guideline, we studied trends in mean systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure, prevalence and burden of hypertension, and proportion of controlled hypertension in the US adult population aged ≥20 from 1999 through 2016. We used data from 38 276 adults from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Age-standardized prevalence of hypertension decreased from 48.4% in 1999-2000 to 45.4% in 2015-2016. However, absolute burden of hypertension consistently increased, from 87.0 million in 1999-2000 to 108.2 million in 2015-2016. The age-standardized proportion of controlled hypertension among adults receiving antihypertensive pharmacologic treatment increased from 1999-2000 (25.6%) to 2015-2016 (43.5%). There was not consistent improvement in control throughout the full period among non-Hispanic blacks, individuals aged ≥60, or those with diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, or high cardiovascular disease risk.
Conclusions: Based on the 2017 guideline, from 1999 to 2016, the age-standardized prevalence of hypertension decreased and the proportion of control among those treated for hypertension improved. However, the absolute hypertension burden increased. Among those treated, the control rate did not consistently improve in all subgroups. These data emphasize the need for continuous efforts in the prevention and control of hypertension in the US general population.
Keywords: epidemiology; high blood pressure; hypertension; risk factor.
© 2018 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley.
Figures
References
-
- GBD 2015 Risk Factors Collaborators . Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1659–1724. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Forouzanfar MH, Liu P, Roth GA, Ng M, Biryukov S, Marczak L, Alexander L, Estep K, Hassen Abate K, Akinyemiju TF, Ali R, Alvis‐Guzman N, Azzopardi P, Banerjee A, Bärnighausen T, Basu A, Bekele T, Bennett DA, Biadgilign S, Catalá‐López F, Feigin VL, Fernandes JC, Fischer F, Gebru AA, Gona P, Gupta R, Hankey GJ, Jonas JB, Judd SE, Khang Y‐H, Khosravi A, Kim YJ, Kimokoti RW, Kokubo Y, Kolte D, Lopez A, Lotufo PA, Malekzadeh R, Melaku YA, Mensah GA, Misganaw A, Mokdad AH, Moran AE, Nawaz H, Neal B, Ngalesoni FN, Ohkubo T, Pourmalek F, Rafay A, Rai RK, Rojas‐Rueda D, Sampson UK, Santos IS, Sawhney M, Schutte AE, Sepanlou SG, Shifa GT, Shiue I, Tedla BA, Thrift AG, Tonelli M, Truelsen T, Tsilimparis N, Ukwaja KN, Uthman OA, Vasankari T, Venketasubramanian N, Vlassov VV, Vos T, Westerman R, Yan LL, Yano Y, Yonemoto N, Zaki MES, Murray CJL. Global burden of hypertension and systolic blood pressure of at least 110 to 115 mm Hg, 1990–2015. JAMA. 2017;317:165–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

