Antimicrobial actions of dual oxidases and lactoperoxidase
- PMID: 29858825
- PMCID: PMC7336354
- DOI: 10.1007/s12275-018-7545-1
Antimicrobial actions of dual oxidases and lactoperoxidase
Abstract
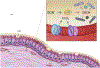
The NOX/DUOX family of NADPH oxidases are transmembrane proteins generating reactive oxygen species as their primary enzymatic products. NADPH oxidase (NOX) 1-5 and Dual oxidase (DUOX) 1 and 2 are members of this family. These enzymes have several biological functions including immune defense, hormone biosynthesis, fertilization, cell proliferation and differentiation, extracellular matrix formation and vascular regulation. They are found in a variety of tissues such as the airways, salivary glands, colon, thyroid gland and lymphoid organs. The discovery of NADPH oxidases has drastically transformed our view of the biology of reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress. Roles of several isoforms including DUOX1 and DUOX2 in host innate immune defense have been implicated and are still being uncovered. DUOX enzymes highly expressed in the respiratory and salivary gland epithelium have been proposed as the major sources of hydrogen peroxide supporting mucosal oxidative antimicrobial defenses. In this review, we shortly present data on DUOX discovery, structure and function, and provide a detailed, up-to-date summary of discoveries regarding antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, and antiparasitic functions of DUOX enzymes. We also present all the literature describing the immune functions of lactoperoxidase, an enzyme working in partnership with DUOX to produce antimicrobial substances.
Keywords: DUOX; LPO; NADPH oxidase; antimicrobial; dual oxidase; lactoperoxidase.
Figures
References
-
- Allen PZ and Morrison M 1966. Lactoperoxidase. Vi. Immuno-chemical studies on lactoperoxidase from the milk of several species. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 113, 540–547. - PubMed
-
- Ameziane-El-Hassani R, Morand S, Boucher JL, Frapart YM, Apostolou D, Agnandji D, Gnidehou S, Ohayon R, Noel-Hudson MS, Francon J, et al. 2005. Dual oxidase-2 has an intrinsic Ca2+-dependent H2O2-generating activity. J. Biol. Chem 280, 30046–30054. - PubMed
-
- Asehnoune K, Strassheim D, Mitra S, Kim JY, and Abraham E 2004. Involvement of reactive oxygen species in toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of NF-κB. J. Immunol 172, 2522–2529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

